Increasing interest in practices like cover cropping and soil health includes challenges across a range of agronomic factors, including pest management.
Increasing interest in practices like cover cropping and soil health includes challenges across a range of agronomic factors, including pest management.
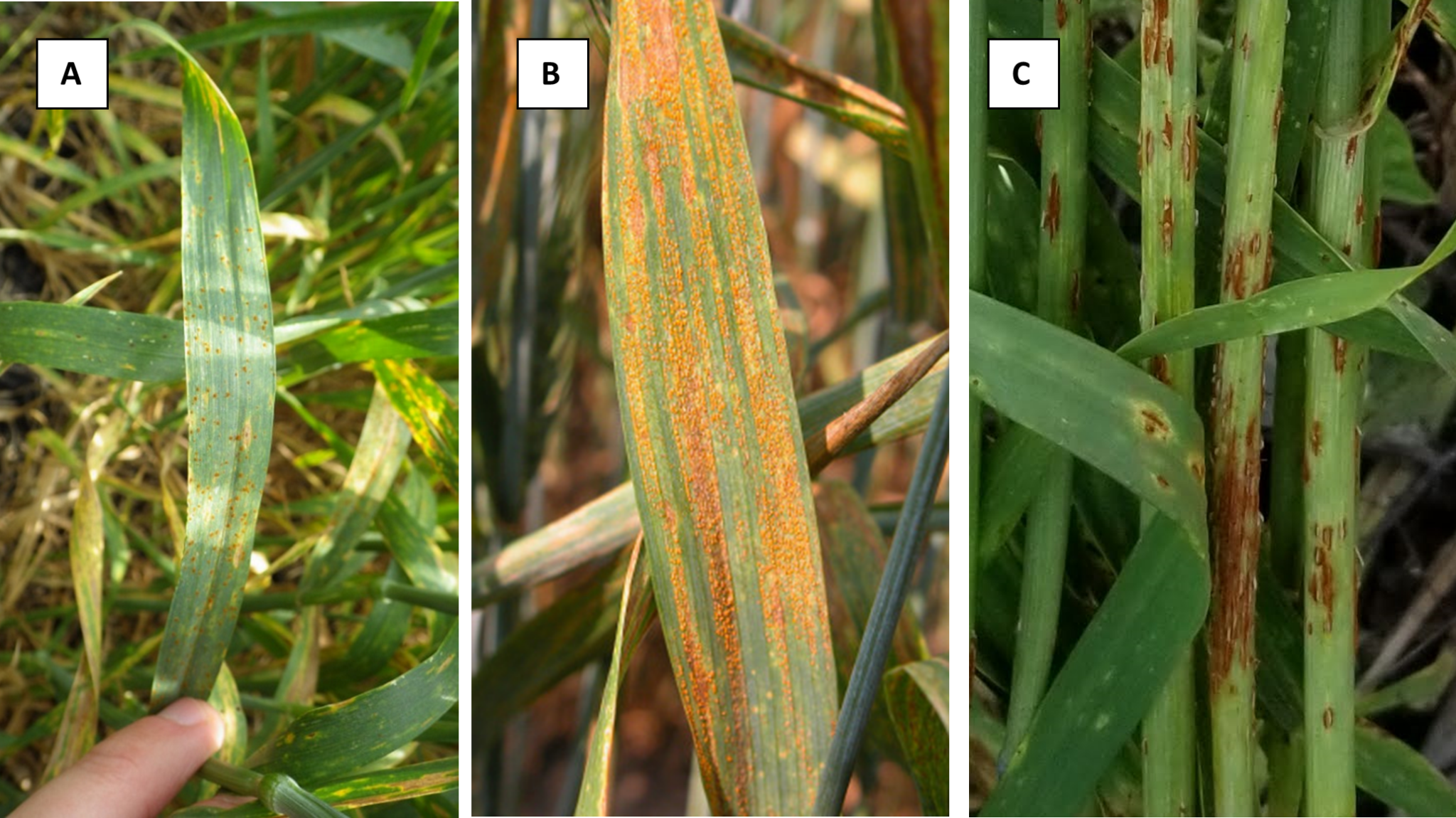

It is time to keep an eye on wheat for diseases and scab risk. There are a number of foliar diseases in wheat to watch out for.

This past fall was a challenge to get cover crops established in many areas of the state due to the dry conditions we had last fall.
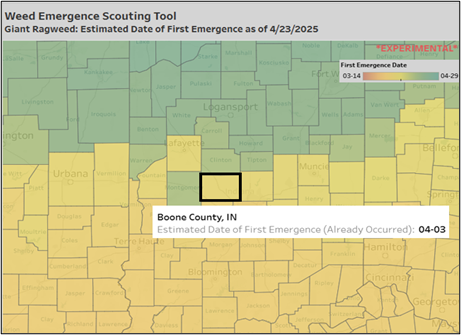
Midwestern farmers have faced a buildup of pesticide resistance in pigweeds (waterhemp and Palmer amaranth), highlighting the importance of scouting to detect weeds early in their growth stages.
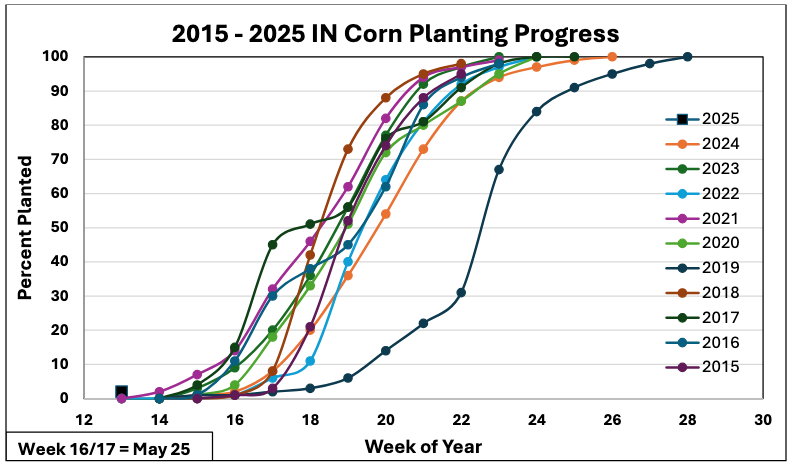
In Indiana, the prime planting window for corn is from April 20 to May 10.

The first seed for the Purdue Corn Team was planted on April 16.
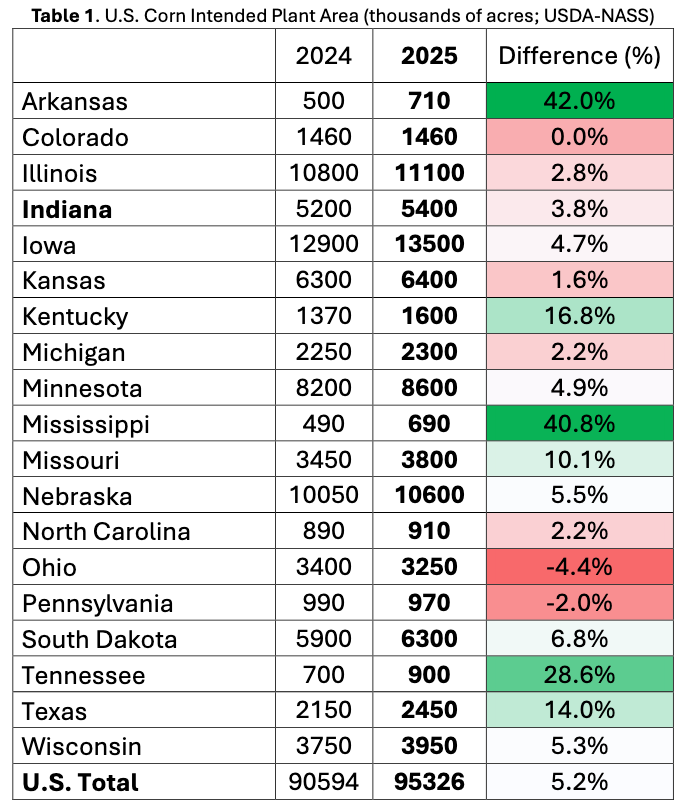
Big news: Corn acres are making a comeback!
After patiently waiting all winter for a warm and sunny break, we’re thrilled to finally have
the chance to get back in the field!
The information presented at this training will provide participants with basic terminology and general knowledge of corn and soybean growth and development, along with pest identification.
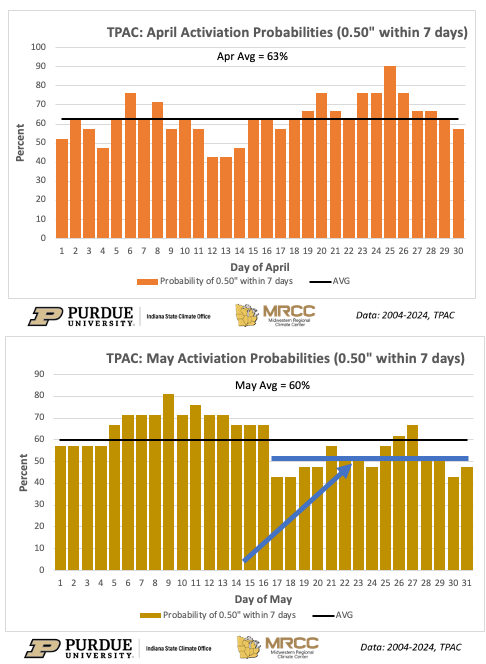
Planting season is getting fully underway across the state, and with that we should all be getting our residual herbicides applied. Residuals are critical to successful season-long weed control as we have less documented herbicide resistance to these chemistries compared to postemergence products, as well as generally we see more consistent control from these herbicides because we’re targeting weeds before they’re even out of the ground. However, for residual herbicides to be successful, they require precipitation to be activated. I frequently get asked how much rainfall is required to fully activate these herbicides, how long can the herbicide wait until we’d receive this rainfall, and if a shallow tillage event would help the situation. These answers can be highly variable across herbicides (Tables 1 and 2), as they are normally dependent on water solubility and soil adsorption of the active ingredients; however, there are some general estimates that can be[Read More…]
© 2026 Purdue University | An equal access/equal opportunity university | Copyright Complaints | Maintained by Pest&Crop newsletter
If you have trouble accessing this page because of a disability, please contact Pest&Crop newsletter at luck@purdue.edu.