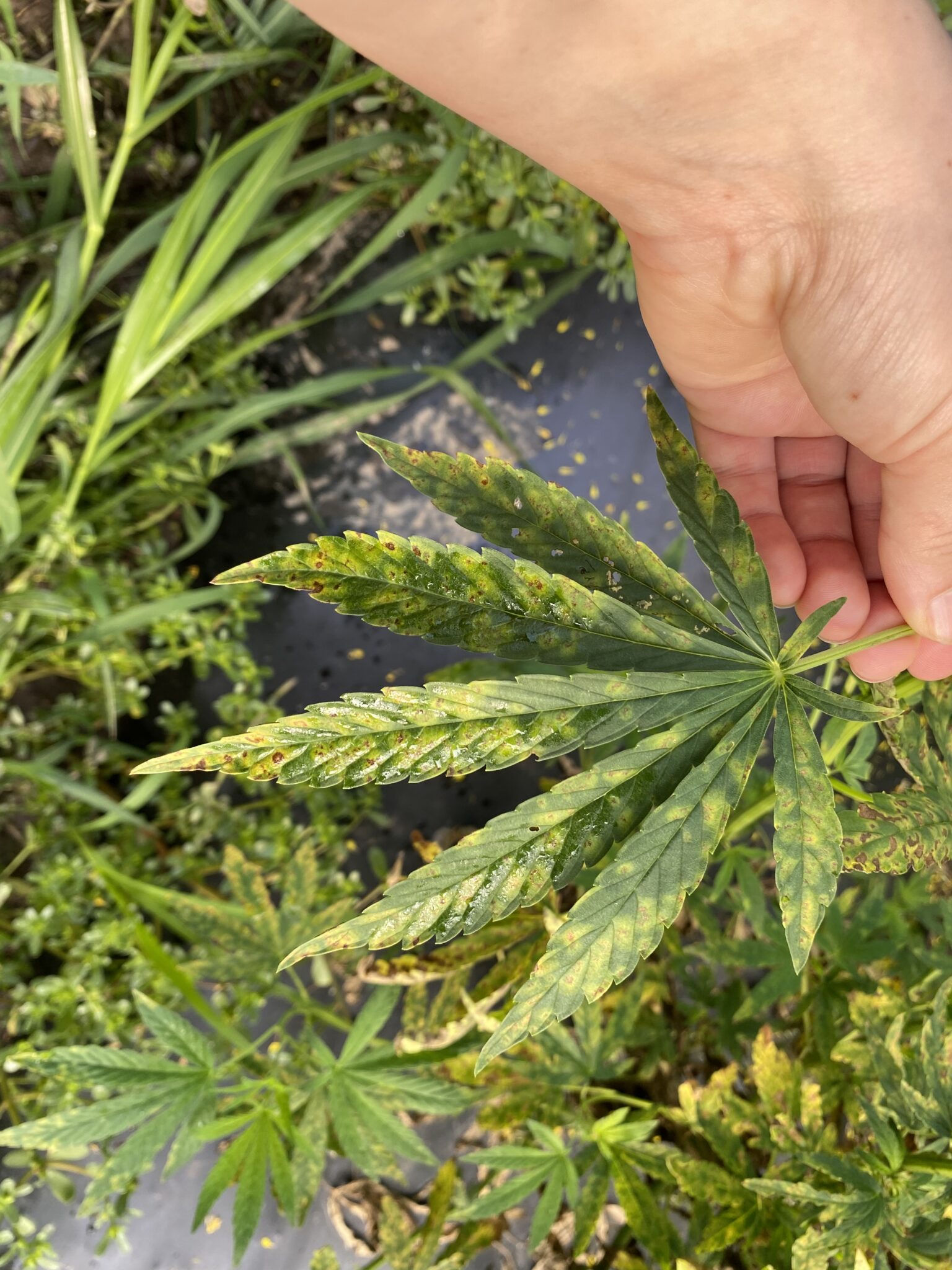

The heavy rain events and somewhat cooler temperatures prior to this week’s heatwave increased disease pressure in hemp.

The heavy rain events and somewhat cooler temperatures prior to this week’s heatwave increased disease pressure in hemp.
2020 Western Bean Cutworm Pheromone Trap Report
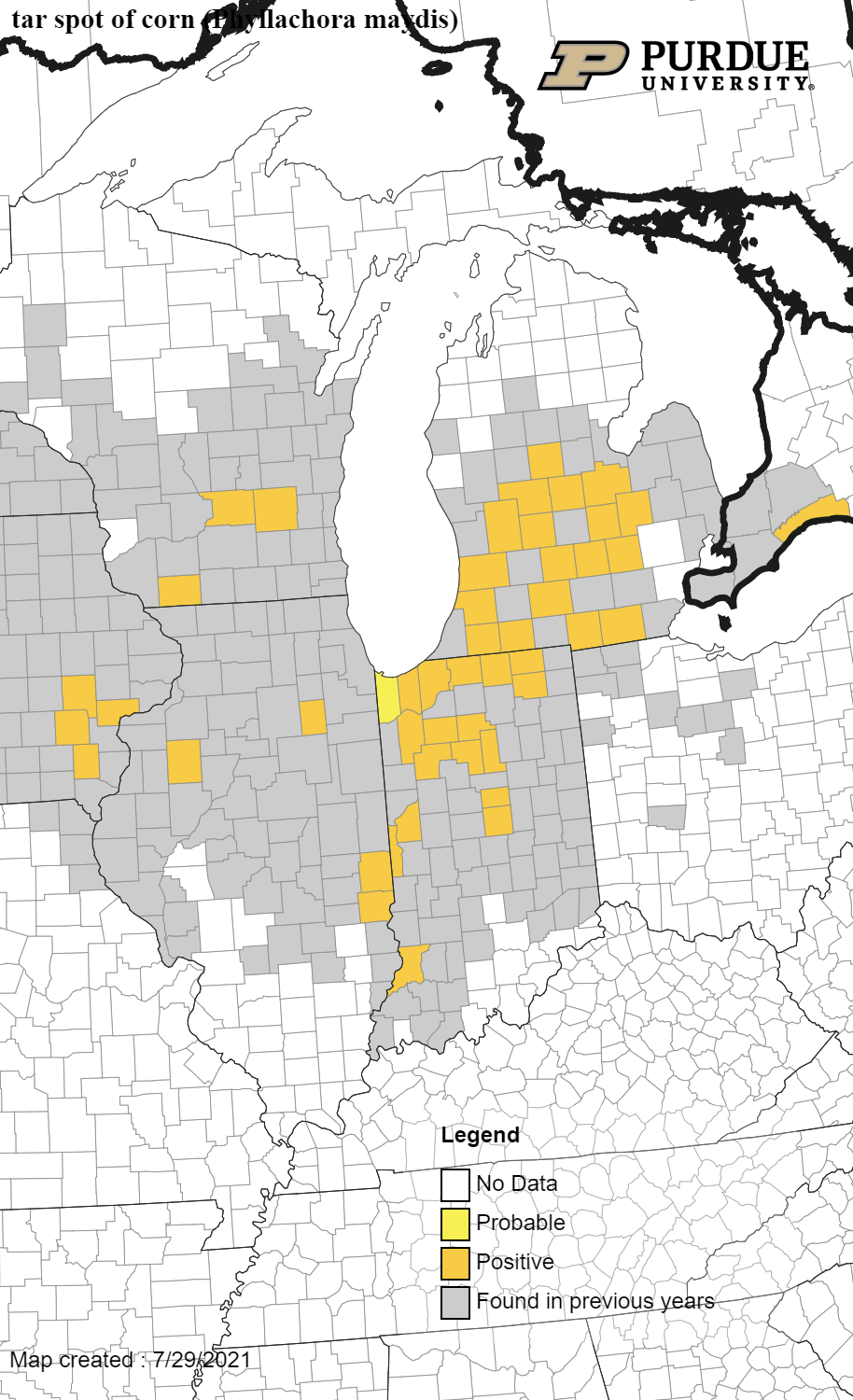
Tar Spot – We continue to confirm counties with active tar spot. Seventeen counties have been confirmed as of July 29, 2021.

I hope you take more time evaluating what forage species and variety of that species should be purchased than the time taken to buy a vegetable at the grocery store. I
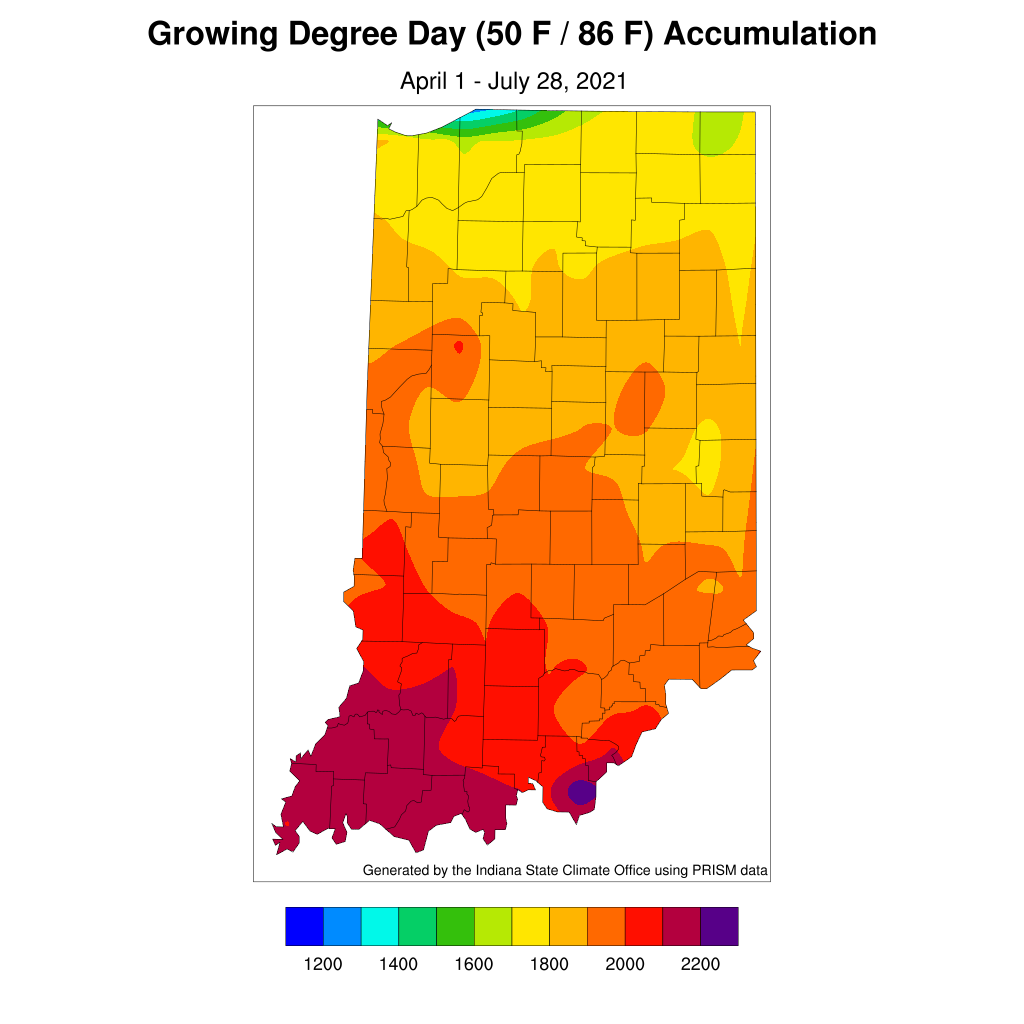
After three consecutive weeks of Indiana being drought free according to the US Drought Monitor, it looks like next month is favored to be drier than normal and cooler than normal.
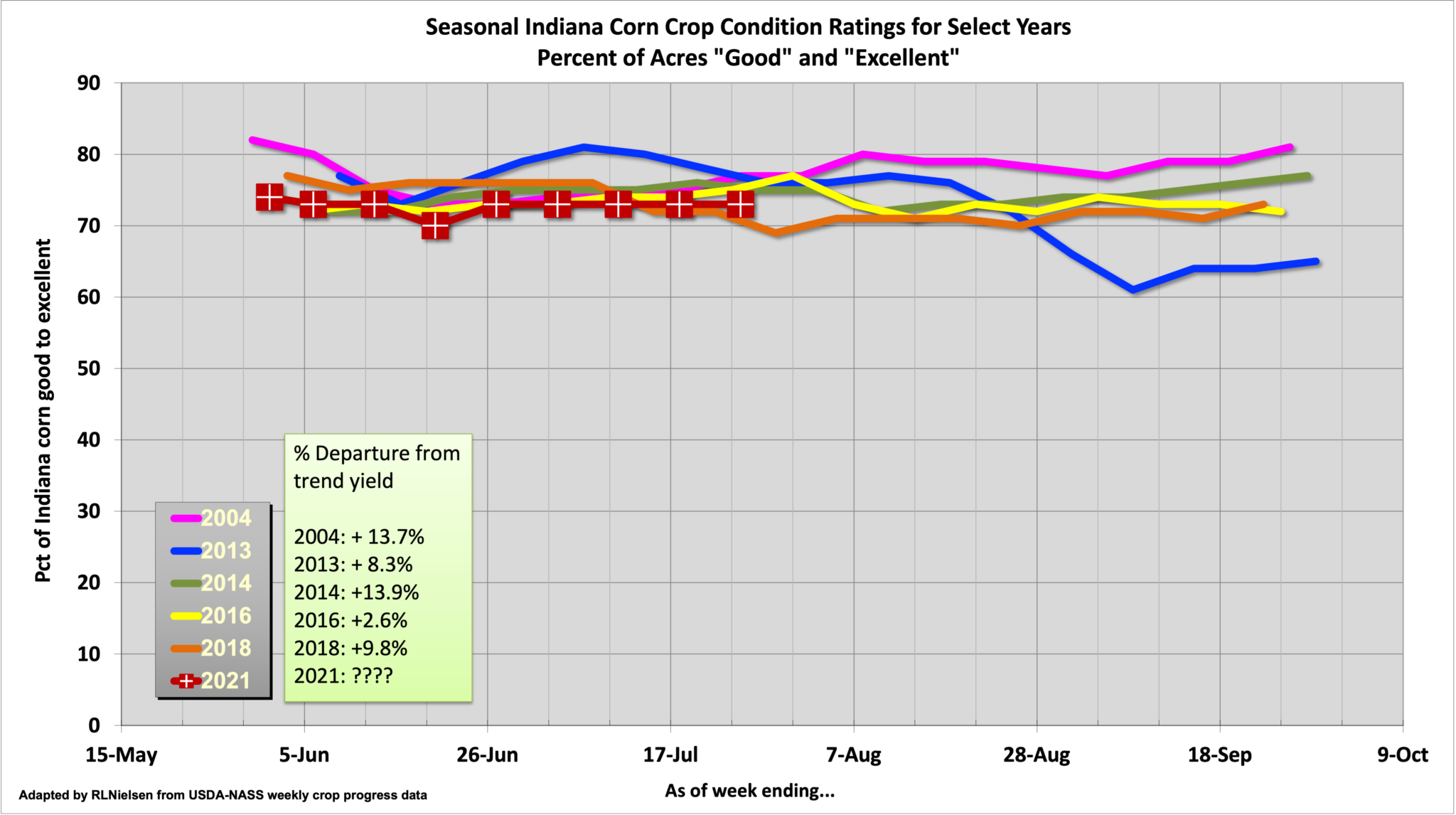
The condition of the 2021 Indiana corn crop, as estimated weekly by USDA-NASS, ranks among the top 6 most recent growing seasons dating back to 2004.
On this Purdue Crop Chat Podcast, Purdue Extension Soybean Specialist Shaun Casteel and Corn Specialist Dan Quinn are joined by Darcy Telenko, Purdue Field Crop Extension Plant Pathologist, to discuss diseases that are popping up around the state in both corn and soybeans.

Corn and soybean growers are very familiar with neonicotinoid seed treatments, and some of the debates that surround their use – including examining their yield benefits and the potential for off-target negative effects.
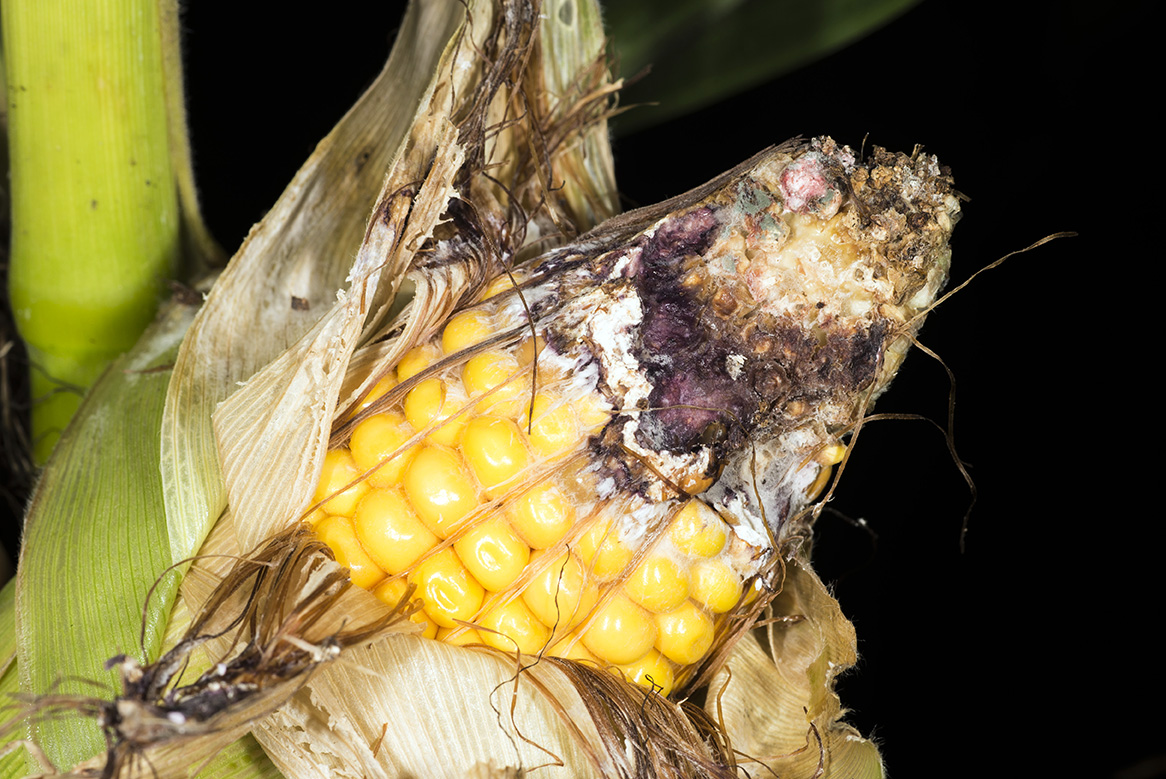

It’s western bean cutworm season – as discussed in last week’s Pest&Crop, moth trap counts are peaking, primarily in Indiana’s northern counties.
Indiana growers have shown increased interest in utilizing cover crops in our corn and soybean production systems over the last decade. Concurrently, there has also been increased utilization of soil residual herbicides to help manage herbicide-resistant weeds such as marestail (horseweed), waterhemp, and giant ragweed in our corn and soybean production systems. Soil residual herbicides can remain active in the soil for a period of weeks to months after application. The length of time a residual herbicide remains biologically active in the soil is influenced by soil texture, soil pH, organic matter, rainfall, and temperature. Since these factors will vary from field to field, definitive time intervals of residual herbicide activity can be difficult to predict. The use of residual herbicides in our corn and soybean production systems may interfere with establishment of fall seeded cover crops under certain conditions. Unfortunately, many of the species being used for cover crops[Read More…]
© 2026 Purdue University | An equal access/equal opportunity university | Copyright Complaints | Maintained by Pest&Crop newsletter
If you have trouble accessing this page because of a disability, please contact Pest&Crop newsletter at luck@purdue.edu.