The Purdue Crop Chat is a regular podcast from Hoosier Ag Today and the Purdue University Extension Service, featuring Purdue Extension soybean specialist Dr. Shaun Casteel and Extension Corn Specialist Dr. Dan Quinn.
Shaun Casteel

Our soybeans have been off to a great start in terms of development this season with 30% of Indiana flowering as of July 7th (USDA-NASS, 2024).
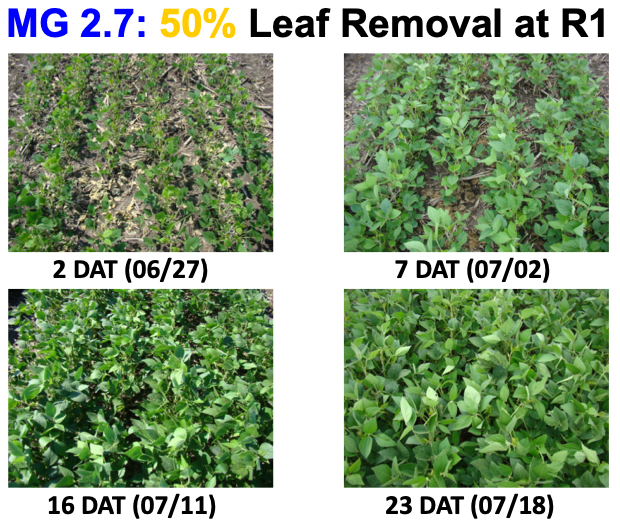
In this video, three different areas of a soybean field that have been subjected to extended periods of saturated soils to flooding are assessed for damage.
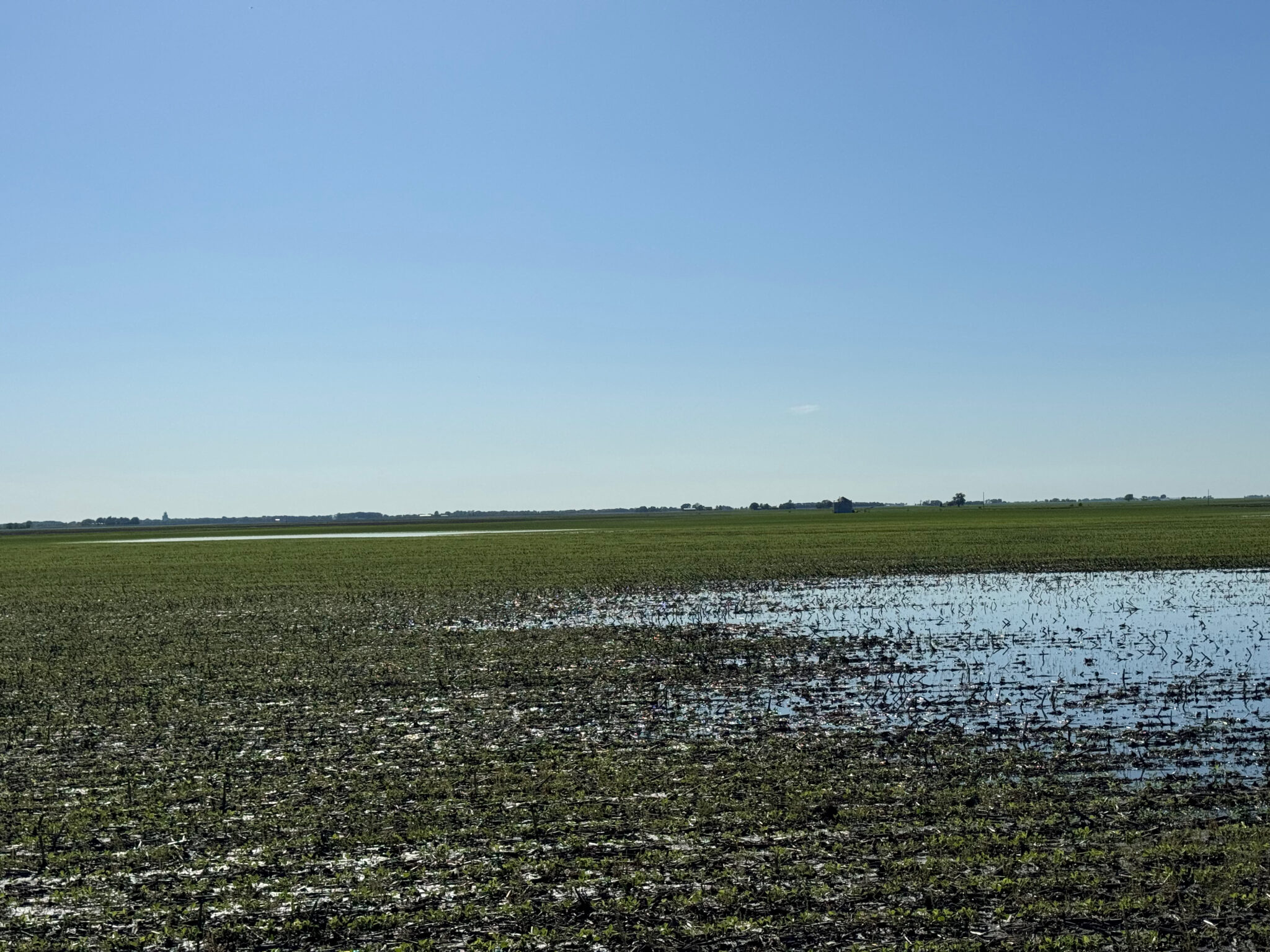

Rains have left many fields with standing water and the threat of more rain on the way. In a manner of a few miles, one field received one inch of rain and another field has received 3 inches of rain or more.
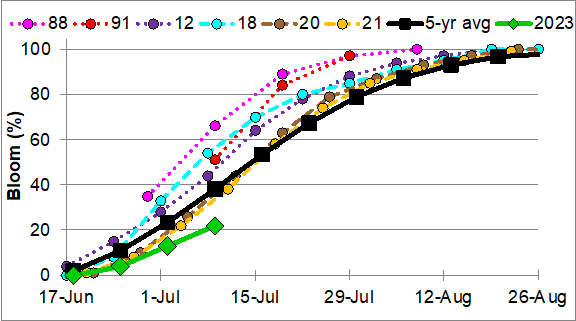
Indiana planting pace in 2023 was one of the fastest on record, which lined up with drought years as well as yield-breaking years. For most of our fields, soybean development in the month of June was summarized in one word – stagnant. Well, at least the aboveground growth seemed to stall out with the dry conditions. Fortunately, these soybeans were rooting down deep rather than expending energy into aboveground growth. If we have our choice of dry June or dry August, we will choose a dry June every time (assuming the roots have some access to moisture). The combination of timely planted soybean with good stand establishment and a dry June sets us up for a nice compact plant. We would rather have a compact plant that has good trifoliate node development and reproductive branches so the water use and photosynthetic efficiencies are optimized during pod development (July-August) and seed[Read More…]
He shares weed management tips and what growers are facing right now.
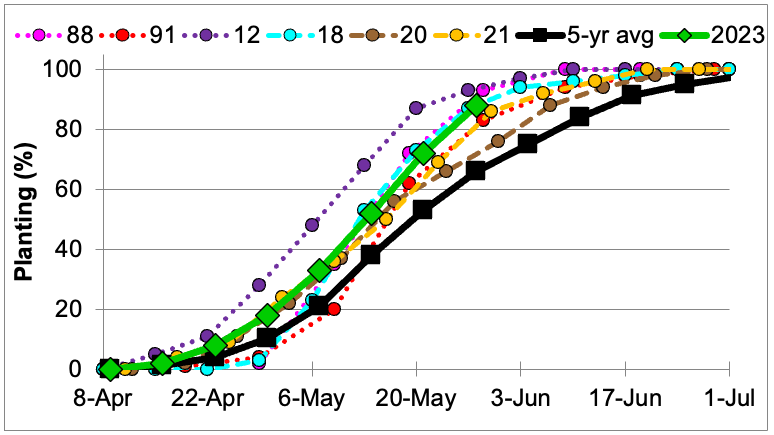
Indiana soybean planting in 2023 is following the same track as 1988 and 2018, which could be devastating or bin busting! As you may or may not recall, 1988 was one of the worst droughts we have experienced. Indiana soybeans yielded 27.5 bu/ac, which was 11.5 bu less (30% reduction) than the trend yield (39 bu/ac). The only year with a faster pace was another drought year—2012. Late season rains saved the 2012 crop and Indiana yielded 44.0 bu/ac (5.8 bu below yield trend, ~12% reduction). Soybeans were planted at a fast pace in 1991 due to dry and drought conditions, but the yields were nearly unaffected (3% less than trend). Indiana has had six years that soybean planting progress was substantially faster than the five-year average (Figure 1). Three of those years were drought years (1988, 1991, 2012) while the other years (2018, 2020, 2021) were yield-breaking[Read More…]

In recent years, a new era in crop management has been centered around biologicals that have targets associated with pest control, improved nutrient supply and uptake, and overall plant growth and resiliency.
On this episode, Shaun and Dan talk about the slow start to the harvest season and some early soybean yield numbers.

On this episode of the Purdue Crop Chat Podcast, Purdue Extension Soybean Specialist Shaun Casteel and Corn Specialist Dan Quinn welcome Indiana State Climatologist Beth Hall to discuss the weather extremes farmers have faced and might continue to face this season.
© 2024 Purdue University | An equal access/equal opportunity university | Copyright Complaints | Maintained by Pest&Crop newsletter
If you have trouble accessing this page because of a disability, please contact Pest&Crop newsletter at luck@purdue.edu.


