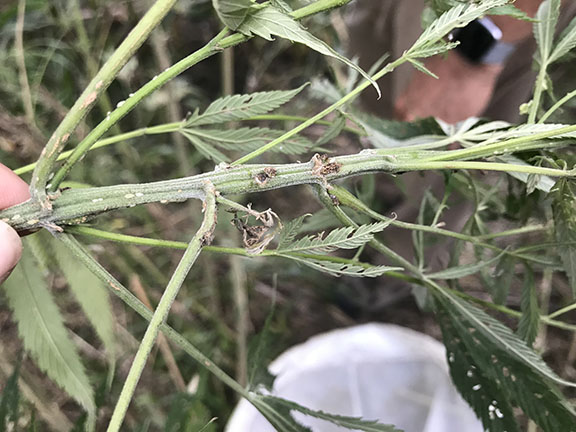

As the growing season progresses and hemp farmers gear up for harvest, we are continuing to learn more about pests and pathogens affecting hemp in Indiana.

As the growing season progresses and hemp farmers gear up for harvest, we are continuing to learn more about pests and pathogens affecting hemp in Indiana.
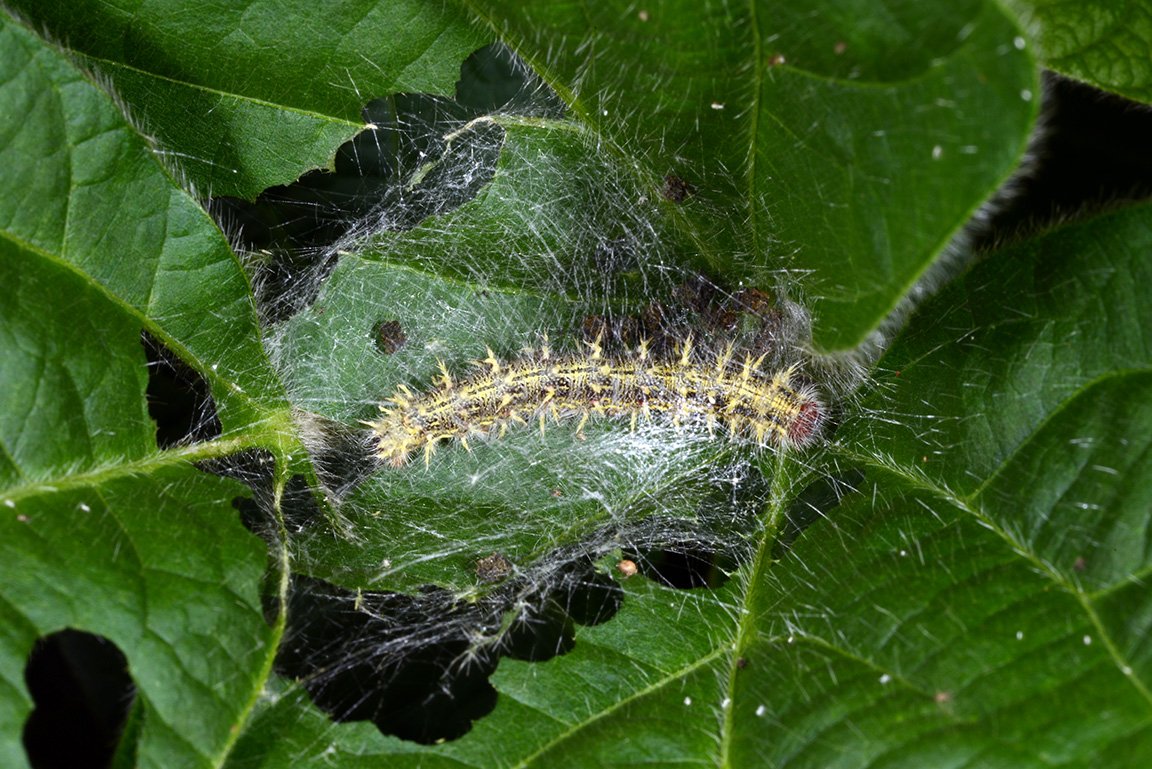

The painted lady butterfly, Vanessa cardui, is mostly orange mottled with black and white markings.
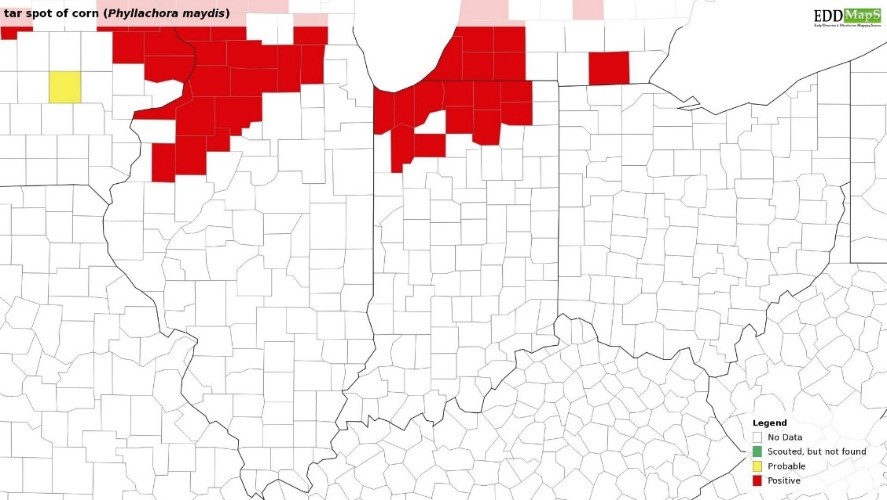
Soybeans We are starting to see a number of diseases in soybean across Indiana. This week in our plots in both northern and southern Indiana initial foliar symptoms of sudden death syndrome are making an appearance. In addition, we continue to see frogeye leaf spot and Septoria brown spot – the levels of both of these diseases were very low and our soybean are about R4 (beginning pod) to R5 (full pod). I suspect that if we continue to receive intermittent rain, we might start to see a bit more disease in soybean. Corn Tar Spot – We have confirmed 11 counties with active tar spot as of August 28 for the 2019 season. These counties all had a previous history: Elkhart, Jasper, Kosciusko, La Porte, Lagrange, Lake, Marshall, Noble, Porter, Pulaski, and St. Joseph (figure 1). I have included the 2018 tar spot map from Indiana for your reference[Read More…]
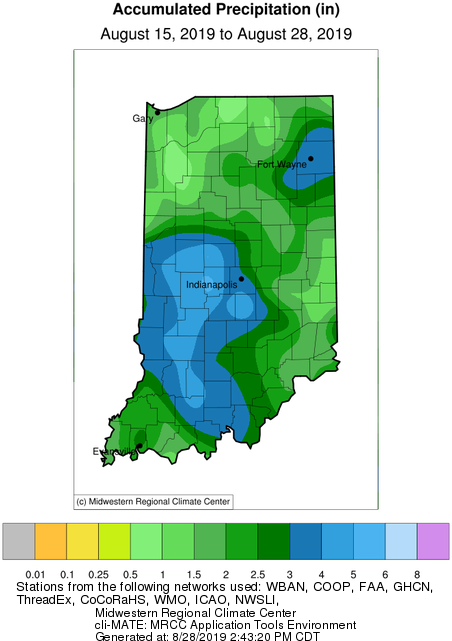
The big story this week was the much-needed rain throughout most of Indiana that fell on Monday (August 19th).

2019 Corn Earworm Trap Report
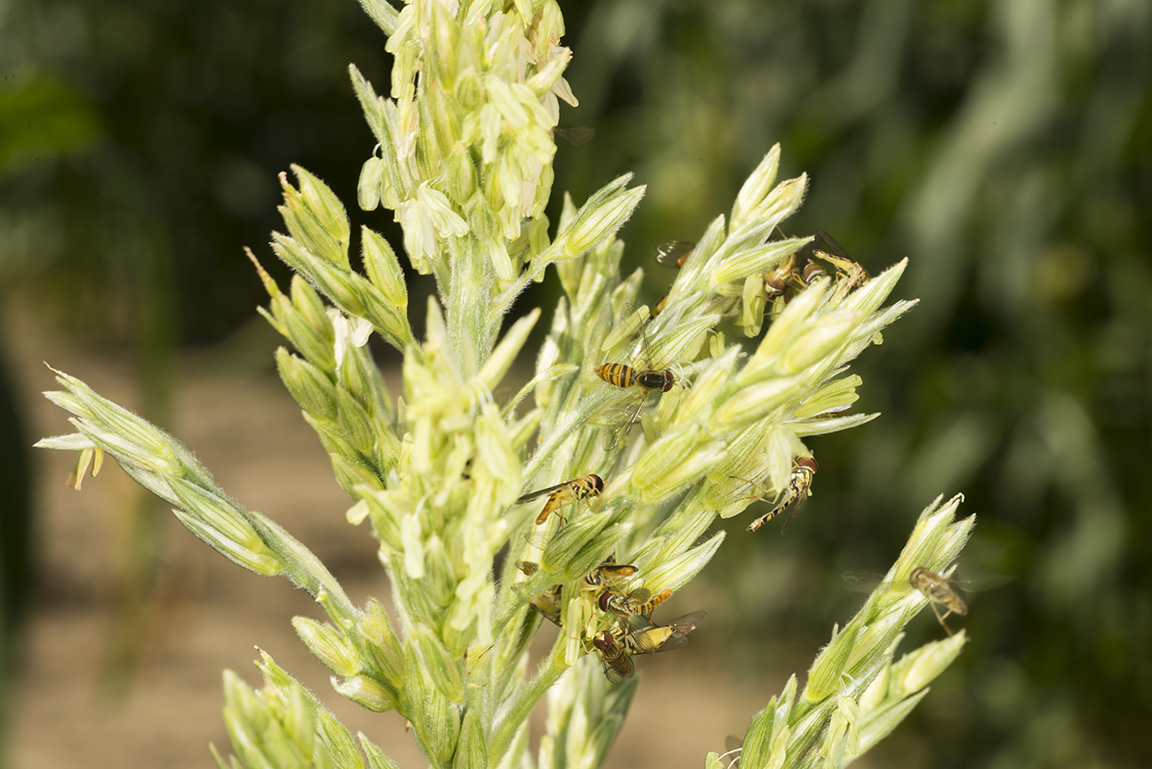

Recently there have been numerous reports of swarms of “bee-like” flies around Indiana fields, farmsteads, and rural environments, and wanted to take the opportunity to tell you a bit about this curiosity. Adult hover flies (aka syrphid flies) can sometimes be mistaken for bees or wasps, because they look a lot like them! Some people refer to hover flies as “corn flies” or “sweat bees,” but these insects are actually quite different from bees. Hover flies belong to the Order Diptera, or the true flies. The most noticeable group at this time of year belong to the genus Toxomerus, which feed on pollen. There are many other syrphid flies present throughout the season that are beneficial, as their larvae feed on soft-bodied insects like aphids. Compared to sweat bees, hover flies have black and yellow markings, are able to fly in place yet dart away quickly, have a[Read More…]

2019 Corn Earworm Trap Report
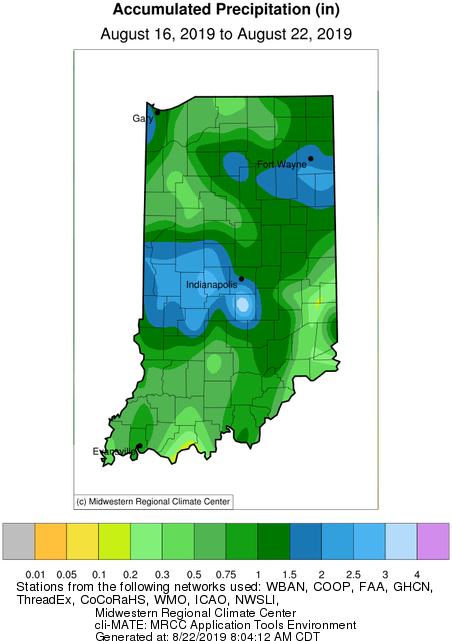
Sporadic rain events are barely bringing relief to sections of Indiana .
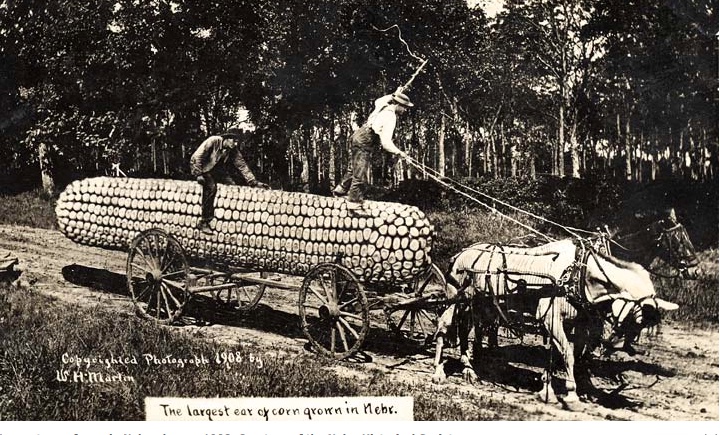

Fancy colored yield maps are fine for verifying grain yields at the end of the harvest season, but bragging rights for the highest corn yields are established earlier than that down at the Main Street Cafe, on the corner of 5th and Earl.
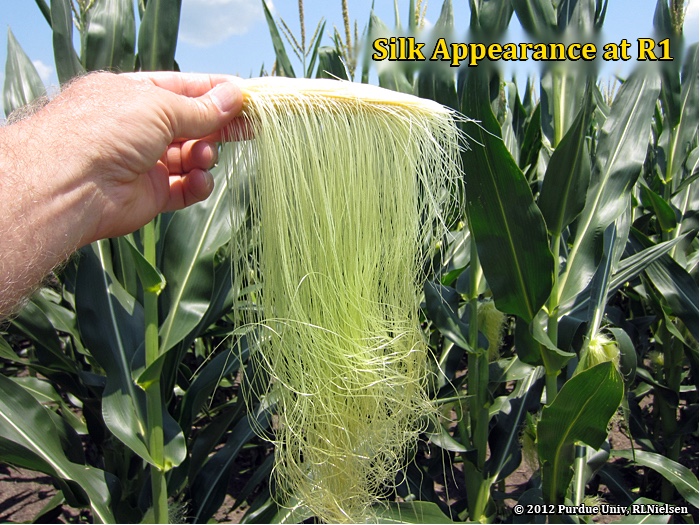

The grain fill period begins with successful pollination and initiation of kernel development, and ends approximately 60 days later when the kernels are physiologically mature. During grain fill, the developing kernels are the primary sink for concurrent photosynthate produced by the corn plant.
© 2024 Purdue University | An equal access/equal opportunity university | Copyright Complaints | Maintained by Pest&Crop newsletter
If you have trouble accessing this page because of a disability, please contact Pest&Crop newsletter at luck@purdue.edu.