
The consequences of flooding, ponding, and saturated soils on young corn depend heavily on the duration of the stress and temperatures.

The consequences of flooding, ponding, and saturated soils on young corn depend heavily on the duration of the stress and temperatures.
When a freeze occurs early in the spring after soybean fields have been planted, damage is dependent on many variables, especially the growth stage.
On the latest Purdue Crop Chat podcast found here and on iTunes, Purdue Extension Corn Specialist Dr. Bob Nielsen and Soybean Specialist Dr. Shaun Casteel talk about the impact of the frost event over the weekend and if replanting will be necessary.

To make excellent quality hay, the forage needs to be cut at the right growth stage and packaged into a bale at the right moisture content without incidence of rain damage.
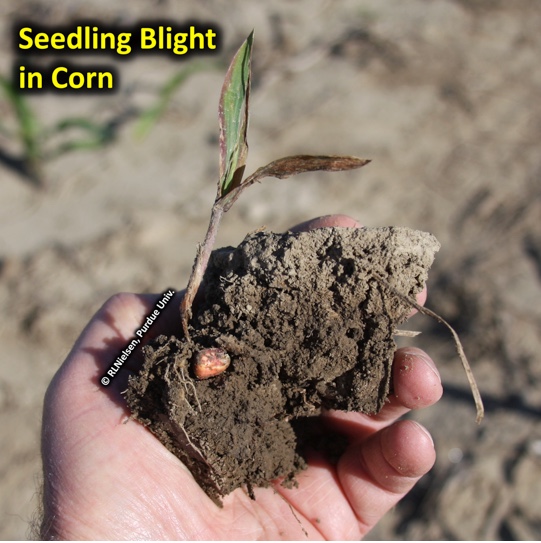

While corn planting progress is way ahead of the miserable 2019 planting season, Indiana’s corn crop has already experienced more than its fair share of misery.
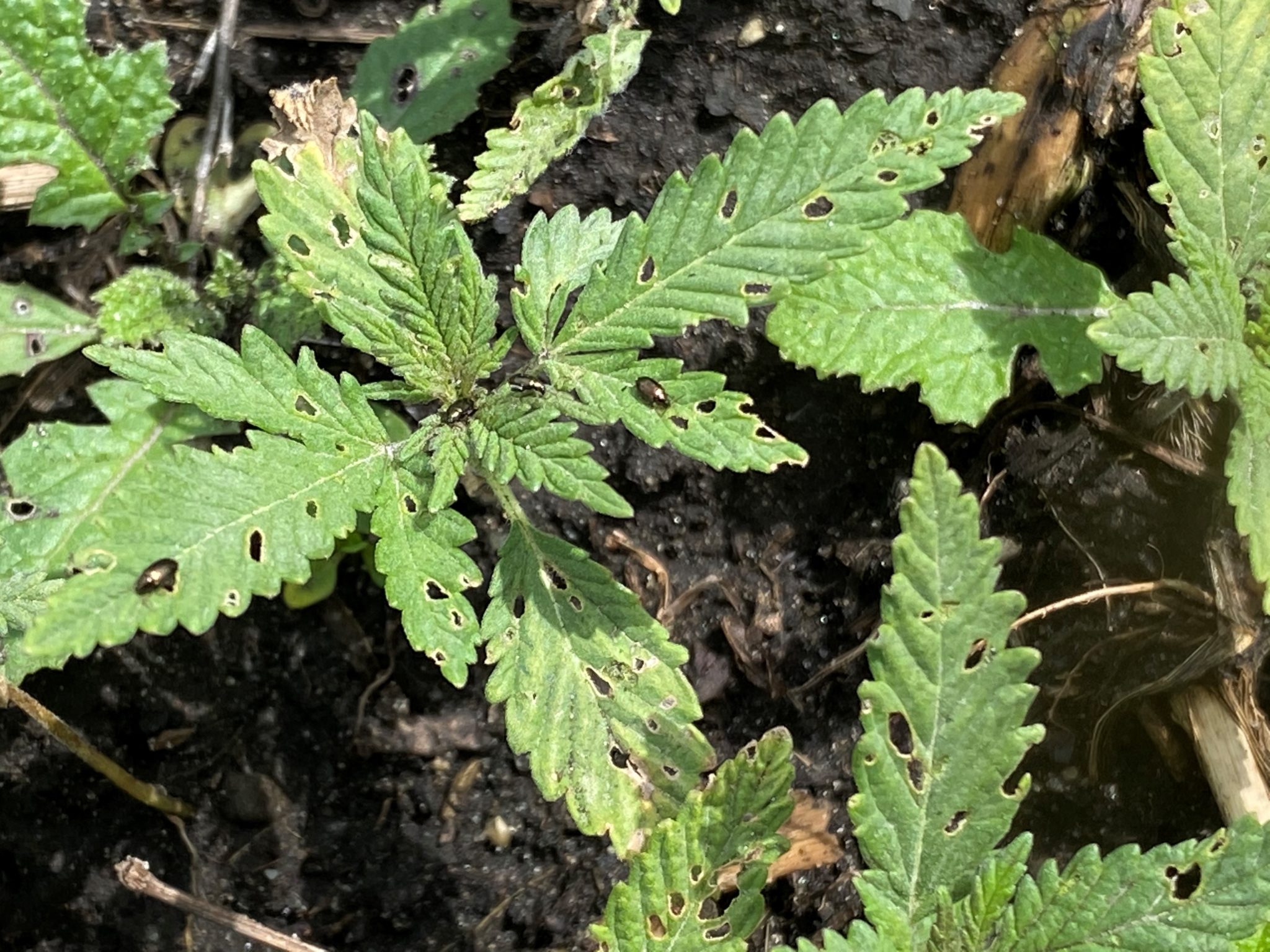

Hemp growers and researchers are preparing to plant hemp in the next two to three weeks across the state. Planting will likely continue until the end of June depending on what type of hemp is being grown.
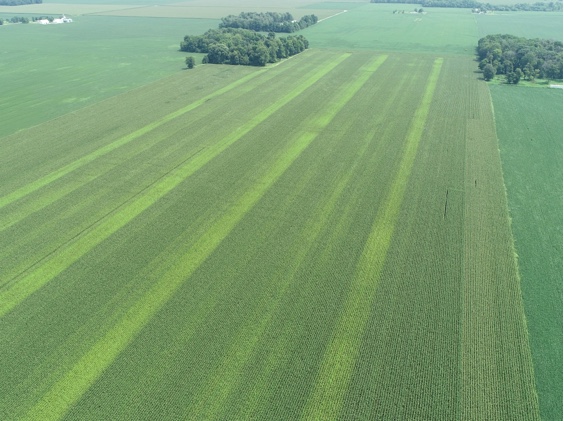

Although nitrogen (N) fertilizer can be costly, it is needed to optimize profit in Indiana cornfields. Applying too little N reduces profit by reducing grain yield. Too much N does not return value and can also damage the environment.
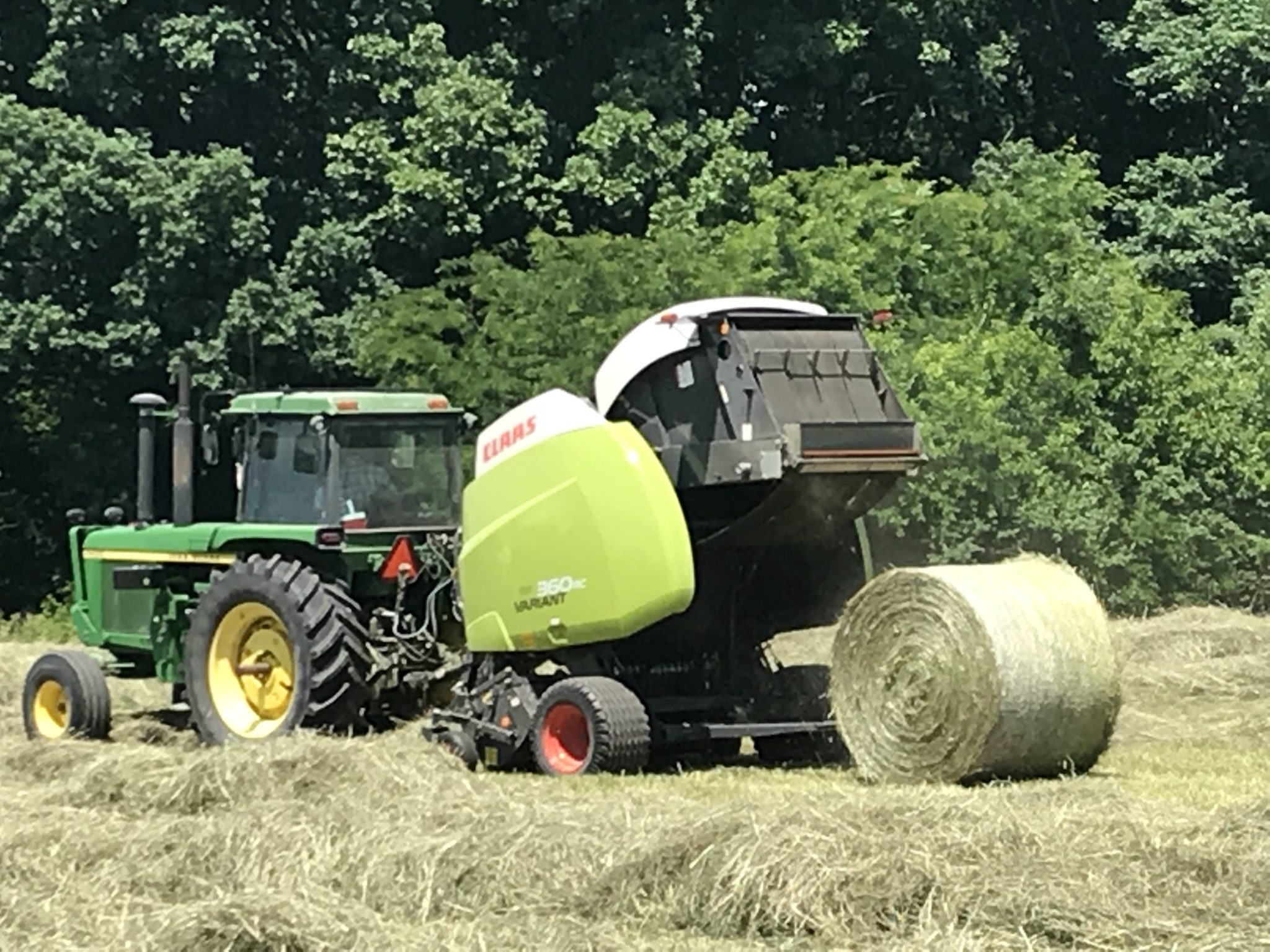

As we near mid-May, it is important to have hay harvest equipment in excellent condition so the forage can be harvested at optimum quality when weather conditions allow and to reduce harvest delays because of equipment breakdowns.
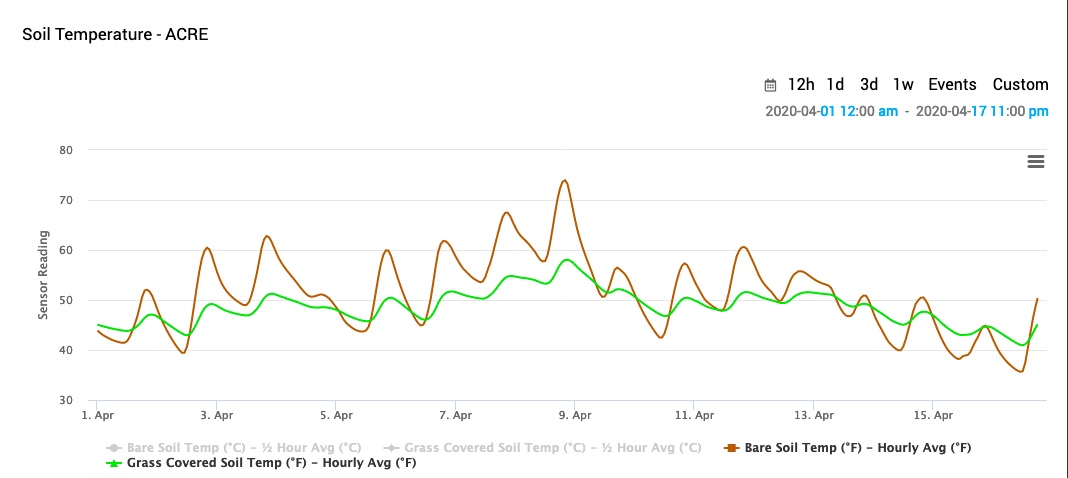
While the coffee shop rumor mills were active this past week with talk of “a lot” of corn planting going in areas of the state, in reality very little planting actually occurred (USDA Weekly Crop Progress, 13 Apr 2020).

The risk of damaging spring frost events is one of the downsides to planting corn earlier than normal, but is one growers often accept when early spring field conditions are otherwise suitable for planting.
© 2026 Purdue University | An equal access/equal opportunity university | Copyright Complaints | Maintained by Pest&Crop newsletter
If you have trouble accessing this page because of a disability, please contact Pest&Crop newsletter at luck@purdue.edu.