In Indiana, the prime planting window for corn is from April 20 to May 10.
10 articles tagged "planting".

The first seed for the Purdue Corn Team was planted on April 16.
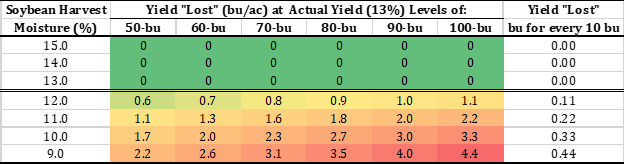
Soybean development in 2024 has been about 10 days ahead the 5-year average from flowering to pod development to leaf drop (USDA-NASS, 2024). Fast stand establishment and high accumulation of heat units (GDDs) during May and June certainly set the pace. Now in many areas, harvest is fully in gear based on the combinations of early maturities, early plantings, and late season heat and dryness. Timely planting is foundational for maximizing soybean production. Growing up in the Midwest, the mindset was to plant corn first followed by soybean (as long as it was planted by Memorial Day you were “fine”). That sentiment has changed based agronomic research, Extension recommendations, and farmers’ experience. Indiana planting of soybean shifted dramatically in 2018 to within ~4 days of corn planting where it had averaged 14 days behind corn the previous ten years. In fact, Indiana farmers continue to place high priority on soybean[Read More…]
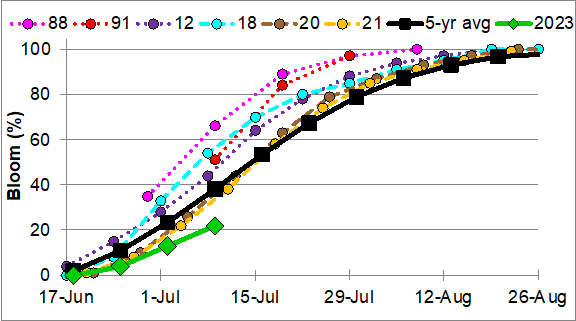
Indiana planting pace in 2023 was one of the fastest on record, which lined up with drought years as well as yield-breaking years. For most of our fields, soybean development in the month of June was summarized in one word – stagnant. Well, at least the aboveground growth seemed to stall out with the dry conditions. Fortunately, these soybeans were rooting down deep rather than expending energy into aboveground growth. If we have our choice of dry June or dry August, we will choose a dry June every time (assuming the roots have some access to moisture). The combination of timely planted soybean with good stand establishment and a dry June sets us up for a nice compact plant. We would rather have a compact plant that has good trifoliate node development and reproductive branches so the water use and photosynthetic efficiencies are optimized during pod development (July-August) and seed[Read More…]
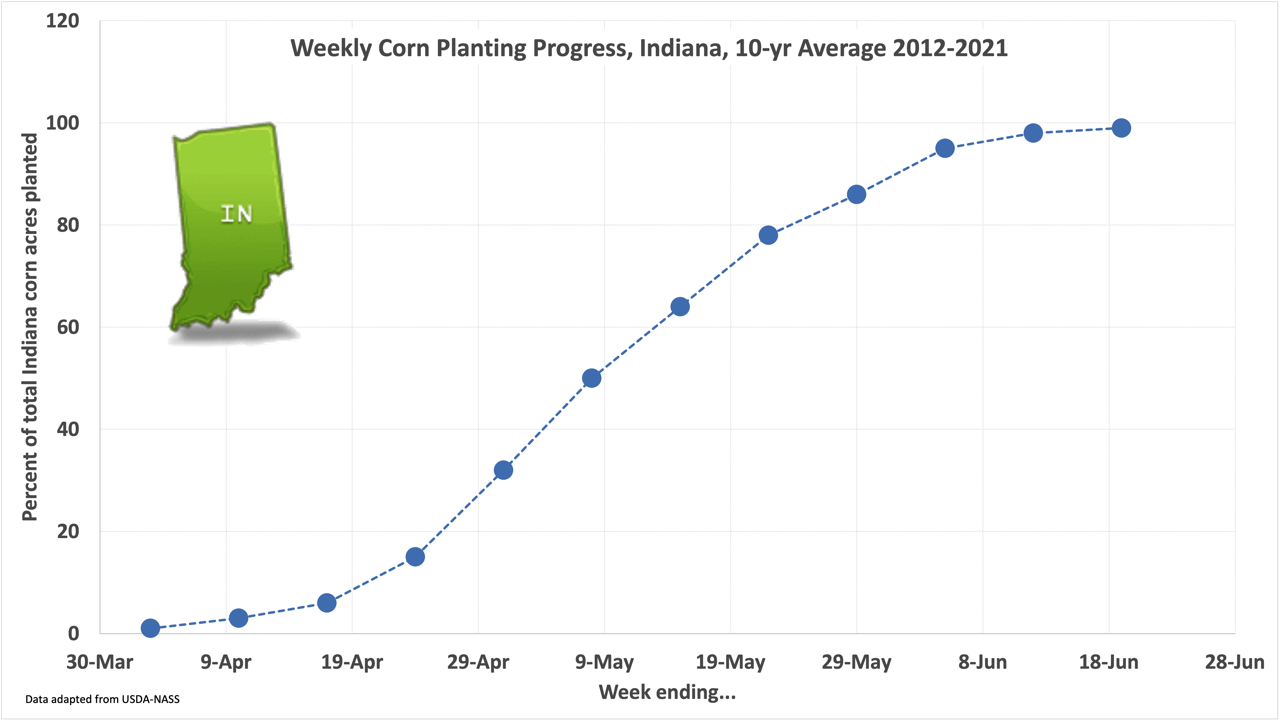
Early planting favors higher yields, but does not guarantee higher yields.
From Commodity classic in New Orleans, the new Purdue Crop Chat podcast comes from the trade show floor with host Eric Pfeiffer and Purdue Extension soybean specialist Dr. Shaun Casteel and Extension Corn Specialist Dr. Dan Quinn.

There is now a new Purdue Crop Chat episode available, and this week #4 talks about the ramp up of planting across Indiana and considerations for seeds going into soil that isn’t quite warm enough for establishing the best stands.
To facilitate speedy planting between rain showers many growers are skipping starter fertilizer. What might be the consequences?
Over the wide variety of planting and soil-applied herbicide situations, most irrigated producers will gain from an early season irrigation application somewhere in the operation most years. The limiting factor is often whether the irrigation system is ready to go.
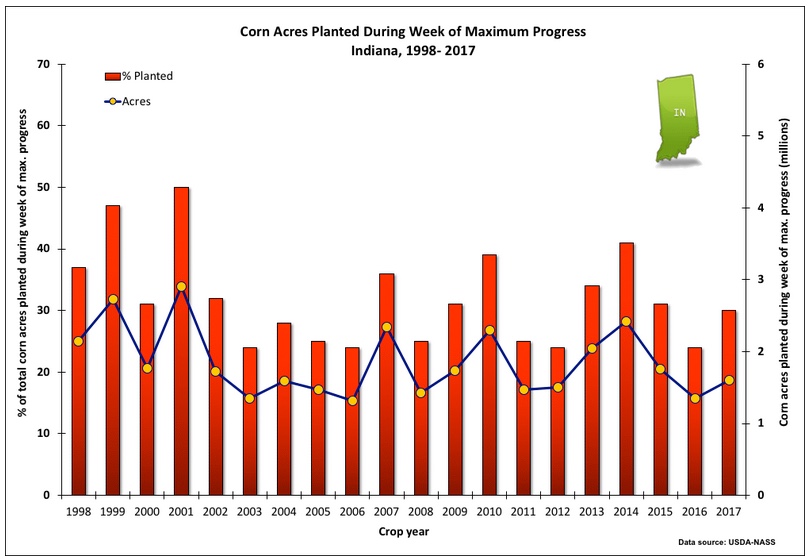
The number of 30-, 40-, and 60-ft wide (or larger) field crop planters across the U.S. Midwest is greater today than, say, twenty years ago. Certainly, individual farmers can plant more acres of corn and soybean per day with today’s large field equipment than they could twenty years ago.


