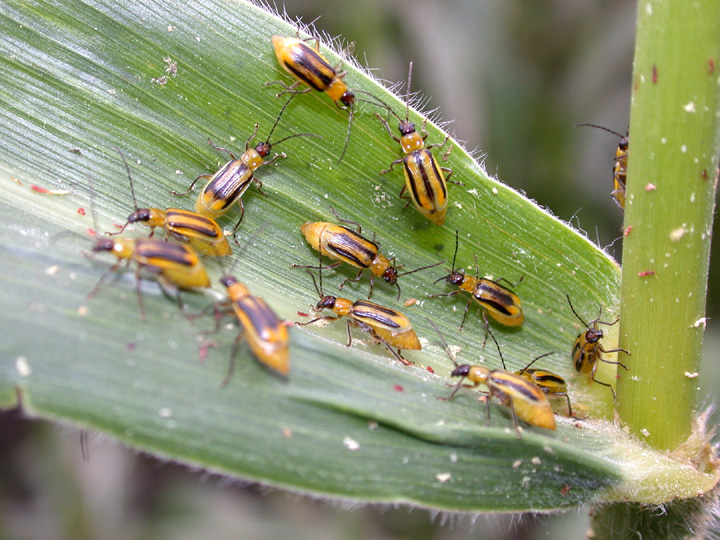
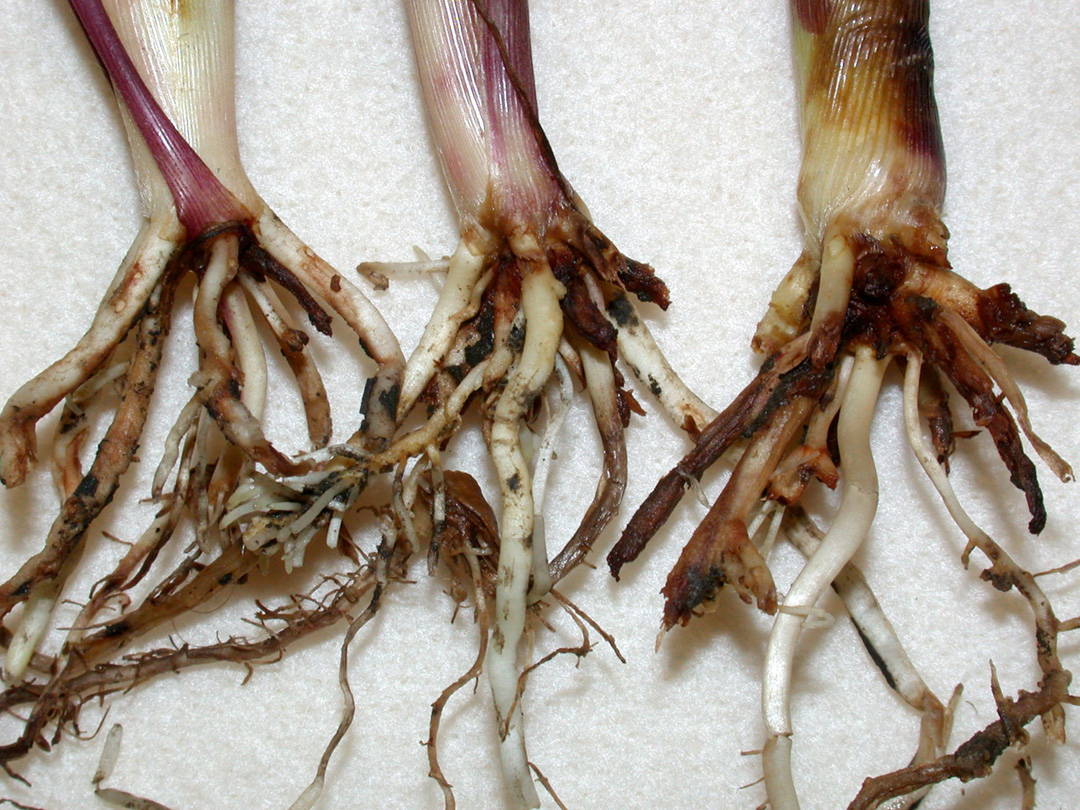
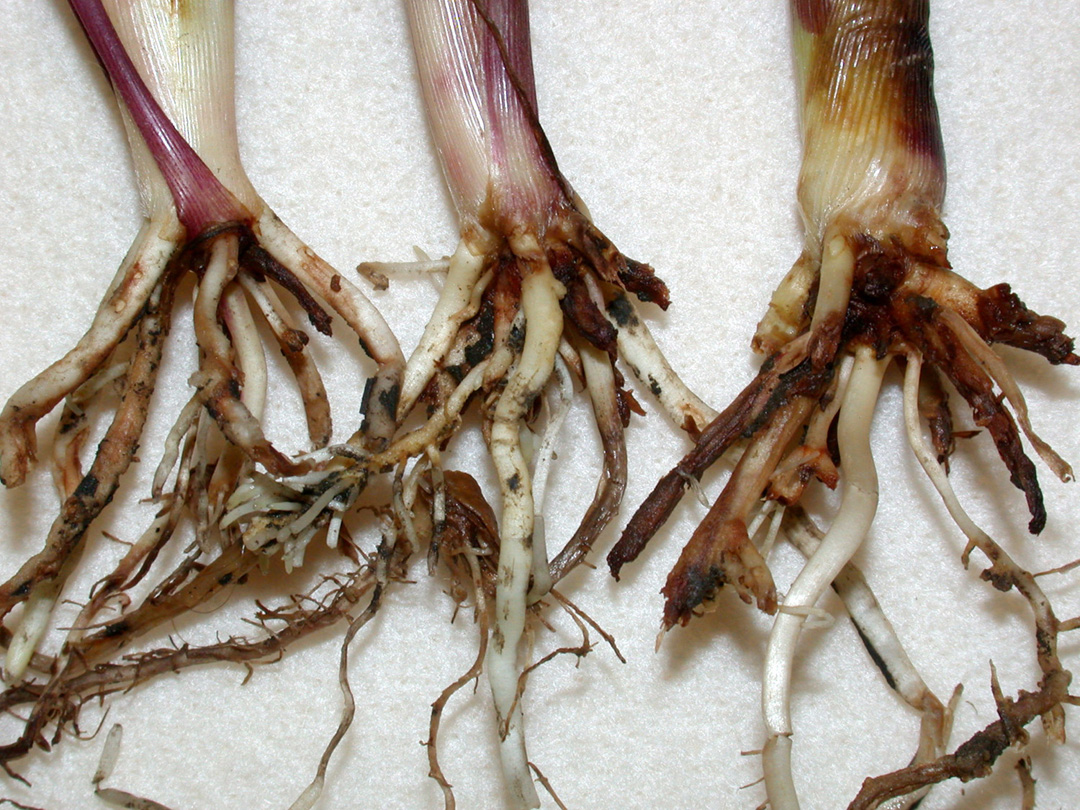
We’ve received multiple reports of impressive rootworm beetle populations in cornfields. Most of these fields were continuous corn without rootworm larval protection. These fields seem to be the exception, but the increasing trend is troublesome. This article is a reminder that is pest is still alive and well. For years, high adoption of highly effective Bt hybrids for rootworm control has likely contributed to a decline in rootworm populations. Overall, Indiana producers have managed this pest through a combination of crop rotation and/or use of Bt-rootworm hybrids. This approach, over many years, drastically reduced rootworm populations compared to 20 years ago. More recently, as state-wide rootworm risks to corn damage declined, producers have used less rootworm protection on their corn. This was a combination of those wanting to save money and take a chance with no protection or those assessing their risks on a field-by-field basis with scouting[Read More…]