Most of Indiana has surpassed the threshold for alfalfa weevil egg hatch and feeding is peaking in southern counties. This means it is time to scout any alfalfa, focusing on the growing tips. If larvae are present, feeding damage will be visible. See the table below for tip damage and treatment guidelines.
Many alfalfa fields will require treatment to manage the larvae. As discussed in this newsletter previously, pyrethroid insecticides are still largely effective, but not bulletproof – resistance has been reported from parts of the US where alfalfa is grown most intensively and weevils are more consistently exposed to insecticides over a larger area.
Refer to the following table and map below for alfalfa weevil development and action steps in your area.
Alfalfa Weevil Management Guidelines Southern Indiana
| Heat Units | % Tip Feeding | Advisory |
|---|---|---|
| 200 | Begin sampling. South facing sandy soils should be monitored earlier. | |
| 300 | 25 | Re-evaluate in 7-10 days using the appropriate HU or treat immediately with a residual insecticide if 3 or more larvae are noted per stem and % tip feeding is above 50% |
| 400 | 50 | Treat immediately with a residual insecticide. |
| 500 | 75 | Treat immediately. |
| 600 | 75+ | If cutting delayed more than 5 days, treat immediately. |
| 750 | If harvested or harvesting shortly, return to the field in 4-5 days after cutting and spray if 1) there is no regrowth and weevil larvae are present OR 2) feeding damage is apparent on 50% of the stubble and weevil larvae are present. |
Alfalfa Weevil (Hypera postica)
Key Degree Day Levels:
• January 1: Start Date
• 300: Egg hatch
• 575: Peak larval feeding
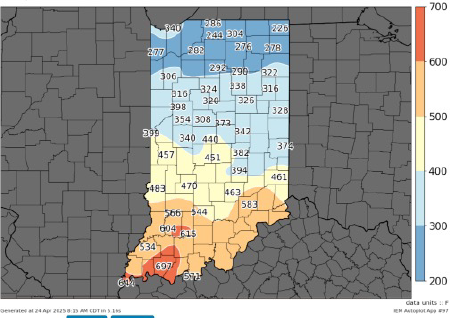
Map generated by: Iowa Environmental Mesonet
https://mesonet.agron.iastate.edu/topics/pests/?state=IN&pest=alfalfa_weevil&sdate=2025-01-01&station=IN0177


