Pest & Crop Newsletter
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Hyper-linked Corn Seedling Insect Diagnostic Guide– (John Obermeyer and Larry Bledsoe) The 2003 field scouting season is here! The following diagnostic guide has been developed to facilitate solving field problems for corn early in the season. Corn symptoms from insect damage are listed below. Possible cause(s) are listed for each symptom. Some problems may have multiple symptoms and/or be caused by multiple pests. A little "detective work" may be needed to diagnose the real culprits! Remember that crop fertility problems, compaction, and disease can mimic symptoms caused by plant pests. Pest names are hyper-linked, clicking on it will link to a page from IPM-1 for further information about the pest, plant damage, scouting methods, and management guidelines. Recommended corn insecticides can be found by clicking HTML or PDF.Happy and accurate scouting!
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Wet Soils and Corn Herbicide Injury Potential- (Bill Johnson, Glenn Nice, and Tom Bauman) The recent wet weather and water-logged soils will increase the possibility of corn injury from soil applied herbicides. Corn growing in wet soils is not able to metabolize (degrade) herbicides as rapidly as corn growing in drier conditions. Plant absorption of herbicides occurs by diffusion. What this means is that the herbicide diffuses from locations of high concentration (application site on the soil) to low concentration (plant roots). The diffusion process continues regardless of how rapidly the corn is growing. In corn that is not growing rapidly, corn plants can take up doses of herbicide high enough to elicit various ranges of symptomology. The unfortunate aspect of wet soil conditions is that additional stress is put on the plant not only to metabolize herbicide residues, but also to ward off diseases and insects. These additional stresses can impact a corn plant’s ability to metabolize herbicide. The most common type of herbicide injury observed under these conditions is associated with chloroacetamide herbicides. These herbicides are used on over 80% of the corn acres in Indiana for control of grass and small seeded broadleaf weeds. These products include the soil-applied grass herbicides such as Dual/Cinch, Degree/Harness/Surpass/Topnotch, Microtech/Lasso, Frontier/Outlook, Define/Axiom and their atrazine premixes. Chloroacetamide Herbicide Mode of Action: Injury Symptoms: After corn emergence (figure 1 left hand side and figure 2). Buggy whipping – leaves may not unfurl properly. In figure 3, this plant is showing both chloroacetamide injury (buggy-whipping) and atrazine injury (necrotic leaf edges and lower leaves completely necrotic). Although atrazine is considered a herbicide with low potential to injury corn, in waterlogged soils with other plant pests present, I have infrequently observed it to injure corn. The good news is that chloroacetamide symptomology occurs fairly frequently even in less stressed environments, particularly with certain hybrids that are more sensitive to chloroacetamide herbicides. However, corn usually grows out of the symptomology once the soil dries and warmer weather prevails. How to Avoid Injury with Chloroacetamide Herbicides: Use proper rate for soil type. Avoid planting too early into cool soil. Consult with seed company representative and avoid hybrids with increased sensitivity to these herbicides on poorly drained soils.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
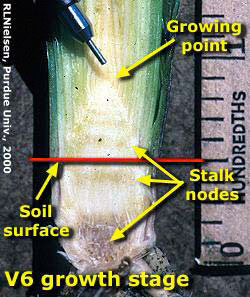
Assessing Corn Recovery From Early-Season Damage- (Bob Nielsen)
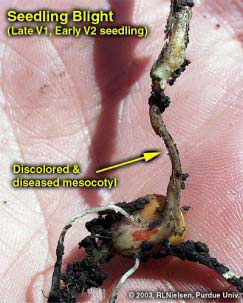
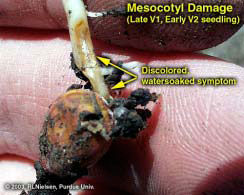
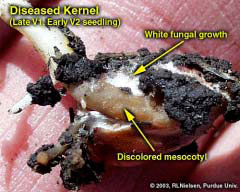
Corn fields are frequently exposed to damaging stresses that can cause extensive plant death or stunting. Your responses to crop damage, including replant and marketing decisions, often require an estimate of the yield loss that may result from the damage. An estimate of yield loss usually requires an assessment of the ability of the corn plants to recover from severe stress and produce harvestable grain. Fortunately, corn has an amazing ability to recover from severe foliar damage early in the season, especially if the plant’s growing point region is undamaged. The growing point region remains below ground until about growth stage V5 or V6 (five to six visible leaf collars); by which time stalk elongation begins and soon elevates the growing point region above the soil surface. From VE (emergence) to about V5 or V6, the only plant tissue exposed above ground is the rolled up leaf tissue of the whorl. Damage to the whorl itself rarely results in plant death. As long as the growing point region is below ground, it is relatively well protected from aboveground damage by hail, wind, frost, aboveground insect feeding, and foliar fertilizer burn. Conversely, while the growing point region is below ground, it is vulnerable to belowground stresses, including saturated soils, soil-borne diseases, and belowground insect feeding. Assessing the ability of young corn plants to recover from severe damage is very much dependent on the health of the growing point region. If the growing point is healthy and the injury is restricted to the aboveground whorl leaf tissue, the damaged plants will almost certainly recover with little, if any, yield loss at the end of the season. If the growing point itself is injured, then successful recovery is much less certain. Occasionally, it is difficult to visually determine the health of the growing point region. Sometimes its appearance (yellowish-white and firm versus discolored and mushy) clearly indicates whether it is healthy or injured. Sometimes the apparent health of the growing point region is not obvious and only time will tell whether it has been truly damaged. If belowground damage targets the kernel (disease, insects), mesocotyl (disease, insects), or seed roots (disease, insects, fertilizer burn) rather than the growing point itself, the prognosis is very much dependent on growth stage of the crop at the time the damage occurred. At early leaf stages (VE to V3), young corn seedlings are very much dependent on the energy reserves in the kernel. From V3 onward, the developing nodal root system increasingly takes over the responsibility for nutrient and water uptake and the plants’ dependence on the energy reserves of the kernels increasingly dwindles. Consequently, damage to the kernel or mesocotyl from VE to V3 will usually kill or severely stunt plants. Damage to the same plant parts after V3 will primarily stunt plants, although decreasingly so with damage to progressively older plants. Patience and time are two key factors that influence your ability to assess the recovery potential of a damaged field for the purposes of making a replant decision. The ghastly appearance of a hail-damaged field the day after the storm can be gut-wrenching. Similarly, the dead tan leaves of young corn plants damaged by frost offer no hope of recovery to many farmers. In times like these, it is prudent to remember what Yogi Berra once said, “It’s not over until it’s over.” Within three to five days following a damaging storm or other severe stress event, fresh leaf growth will be visible from within the whorl of surviving plants. Plants whose growing point regions have been mortally injured will show little evidence of recovery from the whorl. Warm weather during these three to five days following the damage will hasten both the recovery of the survivors and deterioration of the mortally wounded plants. Conversely, cool temperatures in the days following the damage will slow both the recovery and deterioration; and force you to wait a few more days before making an accurate assessment of the field. Related References:Nielsen, Bob. 2000. Growing Points of Interest. Purdue Univ. Corny News Network. Online at http://www.kingcorn.org/news/articles.00/
Effects of Flooding or Ponding on Young Corn- (Bob Nielsen)
Recent intense rainfall events (technically referred to as “toad stranglers” or “goose drownders”) have caused flooding of low-lying corn fields or ponding in poorly drained swales within fields. Other areas within fields, while not technically flooded or ponded, may remain saturated for lengthy periods of time. What are the prospects for recently planted or emerged corn? For corn that has been recently planted, but is not yet emerged, the obvious risk is with surface soil crusts that may develop following a severe downpour. The risk is particularly high for conventionally tilled fields. Corn emergence can be especially challenging when a dense surface crust “sets up.” The resistance of a crust to coleoptile penetration often results in corkscrewed mesocotyl elongation below the surface and eventual leafing out underground if coleoptile emergence is delayed long enough. Monitor high-risk fields where corn emergence has not yet occurred and be prepared to use a rotary hoe if necessary to break up the crust and aid emergence. Don’t dawdle on using the rotary hoe until the crust has baked dry into “concrete.” Operate the hoe at a good speed and do not worry about the occasional corn seedling that is flipped out of the soil. A side benefit to breaking a dense soil crust is the resulting enhanced soil aeration. The “wet feet” caused by flooding or ponding creates other risks for corn that has already emerged, primarily because soil oxygen is depleted after about 48 hours of soil saturation. Without oxygen, the plants cannot perform critical life sustaining functions; e.g. nutrient and water uptake is impaired and root growth is inhibited. The growth stage of a corn crop greatly influences whether ponding or saturated soils kills, severely stunts, or mildly stunts the corn plants. Plants younger than V6 (six visible leaf collars) are susceptible to damage for two reasons. First of all, the growing point is at or below the soil surface from VE to about V6 and therefore is directly subject to the stress of oxygen-depleted conditions. In plants older than V6, the growing point may be above the water level and the likelihood for survival improves greatly. Secondly, plants younger than V6 are in the process of trying to successfully establish a vigorous root system. Stunting or death of roots by oxygen-depletion can be a major stress for a plant that is not yet fully established. Prior to leaf stage V6, corn can survive only two to four days of flooded or ponded conditions. If temperatures are warm during that time (mid-70s°F or higher) such young plants may not survive 24 hours. Cooler temperatures prolong survival. The likelihood of crop injury is less where the flooded or ponded conditions last less than 48 hours. To confirm plant survival, check the color of the growing point and look for new leaf growth three to five days after water drains from the field. Healthy growing points will be firm and yellowish-white, not mushy and discolored. Plants older than V6 will tolerate ponding or saturated soils longer for essentially the opposite reasons. As plants develop beyond V6, rapid stalk elongation elevates the growing point region above the soil surface and, thus, away from the direct stress of flooded soils. Secondly, an older crop’s root system will simply be larger and consequently the crop can tolerate a certain amount of root death without dying or dramatic stunting. Nonetheless, extended periods of saturated soils plus warm temperatures will take their toll on the overall vigor of the crop. Some root death will occur and new root growth will be stunted until the soil dries to acceptable moisture content. As a result, plants may be subject to greater injury during a subsequently dry summer due to their restricted root systems. Concomitant (I found a new word in the dictionary!) with the direct stress of saturated soils on a corn crop, flooding and ponding can result in significant losses of soil nitrogen through the processes of denitrification and leaching of nitrate N. Significant loss of soil N will cause nitrogen deficiencies and possible additional yield loss. Brouder & Joern (1998) offer guidelines in estimating the amount of nitrogen loss due to saturated soils and making decisions on application of additional nitrogen fertilizer to fields once ponded. Lengthy periods of wet soil conditions favor the development of seedling blight diseases, especially those caused by Pythium fungi (Ortiz-Ribbing, 2001). Poorly drained areas of fields are most at risk for the development of these diseases and so are also at most risk for potential replant operations if significant stand loss occurs due to seedling blight outbreaks. Certain diseases, such as common smut and crazy top, may also become greater risks due to flooding and cool temperatures (Bissonnette, 2002). The fungus that causes crazy top depends on saturated soil conditions to infect corn seedlings. The common smut fungal organism is ubiquitous in soils and can infect young corn plants through tissue damaged by floodwaters. There is limited hybrid resistance to either of these two diseases and predicting damage is difficult until later in the growing season. Other flooding/ponding on-line references:Bissonnette, Suzanne. 2002. Odd Plant Diseases Due to Odd Season. Univ. of Illinois Pest & Crop Bulletin, 6/21/02. Online at http://www.ag.uiuc.edu/cespubs/pest/articles/200213j.html. [URL verified 5/5/03]. Don’t forget, this and other timely information about corn can be viewed at the Chat ‘n Chew Café on the World Wide Web at http://www.kingcorn.org/cafe. For other information about corn, take a look at the Corn Growers’ Guidebook on the World Wide Web at http://www.kingcorn.org.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||