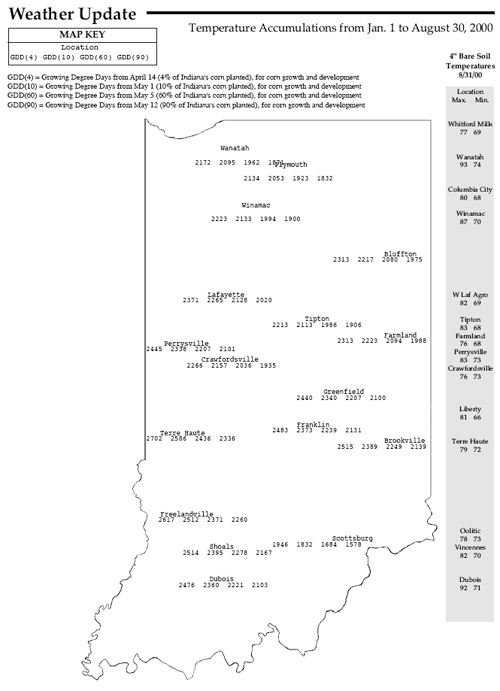
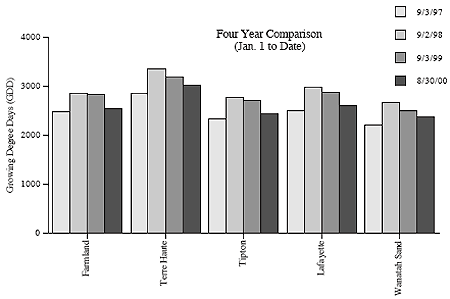
Pest & Crop Newsletter
|
||||||
Corn Insect Pests Beyond the Field– (Linda Mason and John Obermeyer)
While driving county roads it is very apparent that harvest is fast approaching. Yields are expected to be good and storage facilities should be readied for corn that will likely carryover to next summer. Preparing bins for storage now goes a long way toward preventing insect infestations. Several species of insects may infest grain in storage. The principal insects that cause damage are the adult and larval stages of beetles, and the larval stage of moths. Damage by these insects includes reducing grain weight and nutritional value; causing contamination (alive or dead); odor, mold, and heat damage problems that reduce the quality of the grain. Newly harvested corn may become infested with insects when it comes in contact with previously infested grain in combines, truck beds, wagons, other grain-handling equipment, augers, bucket lifts, grain dumps, or grain already in the bin. Insects may also crawl or fly into grain bins from nearby accumulations of old contaminated grain, livestock feeds, bags, litter, any other cereal products, or rodent burrows. Insect infestations can be prevented with good management practices. Now that many grain bins are empty, the following guidelines should be used before the 2000 grain is placed in bins:
|
||||||
Corn Ear Rots in Indiana– (Charles Woloshuk, Dirk Maier)
As corn harvest progresses, it is safe to predict that there will not be any major ear rot and mycotoxin problems in Indiana. The reasons are obvious: rains and mild summer temperatures. We are getting a number of complaints of Diplodia ear rot. Over the past 5 years, Diplodia ear rot has become more of a problem. The reason may have to do with the increase in no-till fields; however, hybrid genetics and weather are major factors. There are no known mycotoxins produced by the Diplodia fungus in the United States. Infection by Diplodia is enhanced by dry weather prior to silking followed by wet conditions at and just after silking. Ears are most susceptible to this disease during the first 21 days after silking. When infection occurs within two weeks after silking, husks prematurely become bleached or straw colored, and entire ears are white to grayish or grayish brown, shrunken, and lightweight. Lightweight ears generally stand upright with the inner husks adhering tightly to each other. Black specks (pycnidia) may be scattered on the husks, cobs and sides of kernels. Ears infected later in the growing season generally have a somewhat uniform whitish to grayish mold growth over and between the kernels starting at the base of the ear and progressing towards the tip. Infected kernel tips are discolored. Some isolates of the causal fungus may cause vivipary (premature germination). Diplodia infected corn will result in potentially significant discounts when graded at the first point of sale. The light kernels will lower the test weight (TW) of a sample. Grade requirements for corn specify a minimum test weight of 56.0 lb/bu for No.1, 54.0 lb/bu for No. 2, 52.0 lb/bu for No. 3, 49.0 lb/bu for No. 4, and 46.0 lb/bu for No. 5. Test weight discounts vary by elevator but are usually around 1 cent/bu for every lb/bu of test weight below 54 lb/bu. Corn kernels in a sample that show damage caused by cob rot, mold infection and surface mold are hand picked out of the sampling screen and graded as part of Total Damaged Kernels (TDK). Grade requirements for corn specify maximum TDK of 3% for No.1, 5% for No. 2, 7% for No. 3, 10% for No. 4, and 15% for No. 5. Damage discounts vary by elevator but are usually around 1 cent/bu for every percent of total damage above 5%. Diplodia infected corn also results in more cobs and kernels being ground up during the combine shelling operation, which results in higher levels of broken corn and foreign material (BCFM). Grade requirements for corn specify maximum BCFM of 2% for No.1, 3% for No. 2, 4% for No. 3, 5% for No. 4, and 7% for No. 5. BCFM discounts vary by elevator but are usually around 2 cents/bu for every percent of BCFM above 3%. Thus, if a Diplodia infected sample graded below 46 lb/bu TW, and above 15% TDK and 7% BCFM, the total discount could easily exceed 30 cents/bu! Farmers should consider making adjustments to combines to minimize the amount of Diplodia infected corn carried into the hopper, as well as adjust concave clearances and speeds to minimize the break up of cobs and kernels. While harvesting a heavily infected field, farmers may also want to take a sample to the elevator for grading before delivering an entire truck load. Corn from heavily infected Diplodia fields should be kept separate from good quality corn during transporting, receiving, wet holding, drying and storage. Infected kernels will also easily break during handling causing an increase in the amount of fine material in a storage bin. These fines will decrease airflow during aeration, which will increase the potential for spoilage. Pre-cleaning especially after drying and before delivery and/or storage is highly recommended to remove the lighter weight damaged kernels, cob pieces, fines and foreign material. This will help to minimize discounts and improve storability of the corn. Proper storage of Diplodia infected corn is crucial. Drying the grain to 15% moisture will stop further growth of the fungus. However, the disease has broken the integrity of the infected kernels. Thus storage fungi, which can grow at 14 to 15 % moisture, such as Aspergillus glaucus, will find it easy to invade the kernels and cause further spoilage damage and self-heating. If Diplodia ear rot is significant, the grain should be dried to below 14 % and cooled to below 50 F as quickly after harvest as possible, and then to 30 F for winter storage. Storage time should be limited to the cold weather season and no Diplodia infected corn should be held into next summer. To prevent a reoccurrence of Diplodia ear rot next year, avoiding reduced-tilled corn following corn is advised. Rotation out of corn will allow corn residue to degrade. One should also consider changing corn hybrid.
|
||||||