
 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| How long can I protect an ash tree with an insecticide application?
Cliff Sadof, Purdue University1 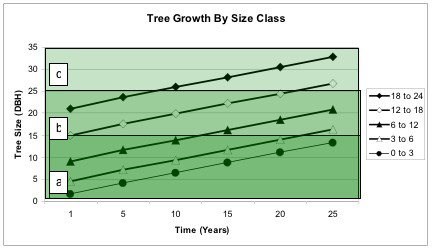 Insecticides are effective tools for extending the life of ash trees during an EAB infestation. Increasing the longevity of a tree provides time for replacement trees to grow and replace lost shade. They also buy time that could allow the development of newer and better controls (insecticides and biological controls) for fighting EAB. The graph above shows how ash trees of different size grow over time. Size is measured as the diameter of the trunk at 4.5 ft above the soil line (DBH). On average, in Indianapolis, the trunk width increases at just under � inch (0.46) per year, or just under a foot (11.5 inches) in 25 years. Each of the five lines in the graph show how a tree in the center of each size range would grow in 25 years. This plot is useful for predicting how long a particular tree can be protected with a given type of insecticide treatment. Annual soil applications of imidacloprid (Bayer Tree and Shrub) and or trunk sprays of dinotefuran (Safari) can protect trees until trunk diameters get to 15� wide at chest height (DBH). This �safe zone� is depicted in the darkest block (a). These insecticides are quite good at protecting small trees. Trees with a DBH between 0-3� can be protected for 25 years, while those with a DBH between 3-6� are protected for about 22 years, and those with a DBH of 6-12� will be protected for about 12 years. Double rates of imidacloprid, applied annually Xytect™, or single doses of Merit® applied twice can protect trees with a DBH of up to 25�. This �safe zone� is depicted in the darker two blocks (a, and b). Trees with a DBH of up to 6-12� can be protected up to 25 years, while those with DBH of 12-18� can be protected for about 21 years and those with a DBH between 18-24 for about 4 years. Please be advised that current restrictions allow only 0.4 lb of active ingredient to be applied to the soil in a given year. This is the equivalent of a single soil drench application to ten trees with a DBH of 12�. Applying more than this amount of imidacloprid per acre is illegal and not advised. Injections of trees with emmamectin benzoate (Tree-äge) every 2 years have also been shown to control EAB in trees with a DBH up to 25�. This �safe zone� is depicted in the darker two blocks (a, and b). Trees with a DBH of up to 6-12� can be protected up to 25 years, while those with DBH of 12-18� can be protected for about 21 years and those with a DBH between 18-24 for about 4 years. Studies of insecticide effectiveness have not yet been reported on trees with a DBH > 25� (block c) so it is hard to say how long this insecticide can protect larger trees. For a more complete discussion of the relative effectiveness of insecticides against EAB, using available delivery methods, please refer to this link How Effective Are Insecticides at Controlling EAB. 1This note was prepared based on the results of insecticide trials conducted at Michigan State University by D. McCullough, and D. Smitley, and at The Ohio State University by D. Herms. Data for building the tree growth model was provided by P. Peper of the USFS. |