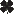|
|
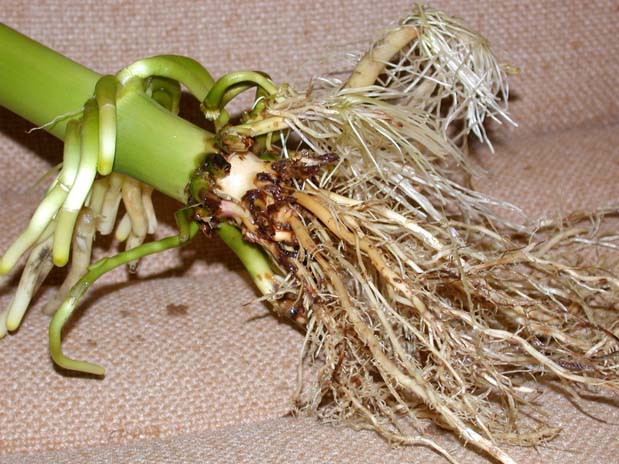
Western Corn Rootroom damage
(John Obermeyer, Purdue University) |
|
Common Name: Western Corn Rootroom - damage
See also: adult | larva Scientific Name: Chrysomelidae: Diabrotica virgifera LeConte Status: serious pest of corn Damaging Stage: larvae and adult beetle Injury: Larvae feed on the roots and root hairs of corn and can reduce crop yield by 10 percent or more. As the roots are destroyed, the plant cannot absorb water. Heavy larval infestations also can cause extreme “goosenecking” or lodging of corn stalks. Adults usually feed on leaf blades where they cause very little damage but they also feed on emerging silks and may interfere with pollination when their populations are high. Action Threshold: Control may be necessary if the silks are being clipped back to 1/2 inch or less before 50% of the plants have been polinated. Management: Western corn rootworms are difficult to manage with chemical controls alone. Often chemicals applied to soil at planting are most effective. Crop rotation practices are a popular cultural method of regulating corn rootworm populations. However, new rootworm variants that can feed in soybean and corn fields are forcing growers to consider new control options such as planting transgenic corn varieties. |
 |
||||||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||
|
Purdue Extension Entomology, 901 West State Street, West Lafayette, IN 47907 USA, (765) 494-4554 Department of Entomology | College of Agriculture | Extension © Purdue University | An equal access/equal opportunity university | Integrity Statement | Copyright Complaints | Maintained by ENTM IT Trouble with this page? Disability-related accessibility issue? Please contact us at entmwebmaster@purdue.edu so we can help. | ||||||||||||||||