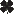|
|
Tussock Moth damage
(John Obermeyer, Purdue University) |
|
Common Name: Tussock Moth - damage
See also: adult | larva Scientific Name: Lymantriidae: several species Status: pest of forest and shade trees Damaging Stage: caterpillar Injury: Newly emerged larvae first feed on the plant tissue in between the leaf veins. However, as they grow and develop, they soon devour all but the main vein and the petiole. Tussock moth larvae attack more than sixty species, but the common hosts are maple, horse chestnut, birch, apple, sycamore, poplar, linden, elm, rose, fir, and larch. Action Threshold: Larvae are usually insignificant pest insects, but certain seasons may warrant control measures. There is no established action threshold, but monitoring should be strict in areas that tend to have tussock moth infestations. Management: In homes, caterpillars can be knocked off walls and ceilings into buckets of soapy water. Outside, caterpillars can be removed from trees with tweezers and knocked into water buckets, though the people doing this are advised to wear long-sleeved shirts to prevent caterpillar hairs from irritating the skin. Insecticides are usually not necessary to control tussock moths. |
 |
||||||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||
|
Purdue Extension Entomology, 901 West State Street, West Lafayette, IN 47907 USA, (765) 494-4554 Department of Entomology | College of Agriculture | Extension © Purdue University | An equal access/equal opportunity university | Integrity Statement | Copyright Complaints | Maintained by ENTM IT Trouble with this page? Disability-related accessibility issue? Please contact us at entmwebmaster@purdue.edu so we can help. | ||||||||||||||||