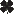|
|
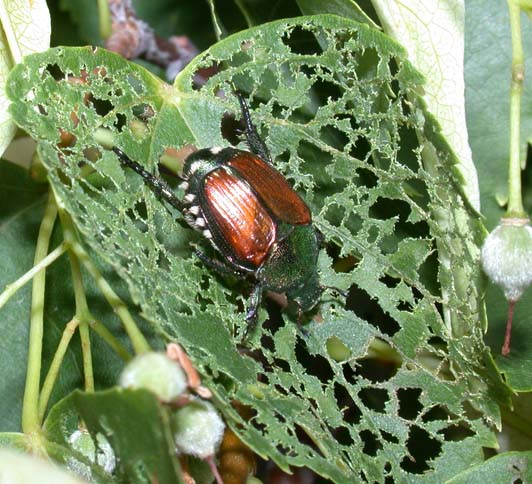
Japanese Beetle damage
(John Obermeyer, Purdue University) |
|
Common Name: Japanese Beetle - damage
See also: adult | larva Scientific Name: Scarabaeidae: Popillia japonica Status: pest of many plants, grasses, and ornamentals Damaging Stage: grub and adult Injury: Adult Japanese beetles may feed on more than 400 different trees, shrubs, flowers, vegetables, and crops. Their damage is usually to the leaves, where they skeletonize the leaf and render it of little value to the plant. Unlike the adults, Japanese beetle grub damage is primarily to grasses. Eggs are laid in the soil, and when they hatch, the grubs prune the roots off of grasses, including both turfgrass and corn. In areas of extensive feeding, the plant turns pale and resembles grass suffering from drought stress. The damage can kill the plant, and in turfgrassses, the turf can actually be lifted and rolled back like carpet. Action Threshold: If plant leaves are decimated by adult feeding, control options should be considered. When sampling the soil, six to eight Japanese beetle larvae recovered per square foot is considered the average action threshold for turfgrass. Management: Japanese beetle adults and larvae can be managed by a number of biological and chemical controls. Extensive adult feeding usually requires chemical maintenance. Lawns that are well-managed can sustain higher larval populations than grass that is under environmental. |
 |
||||||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||
|
Purdue Extension Entomology, 901 West State Street, West Lafayette, IN 47907 USA, (765) 494-4554 Department of Entomology | College of Agriculture | Extension © Purdue University | An equal access/equal opportunity university | Integrity Statement | Copyright Complaints | Maintained by ENTM IT Trouble with this page? Disability-related accessibility issue? Please contact us at entmwebmaster@purdue.edu so we can help. | ||||||||||||||||