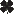|
|
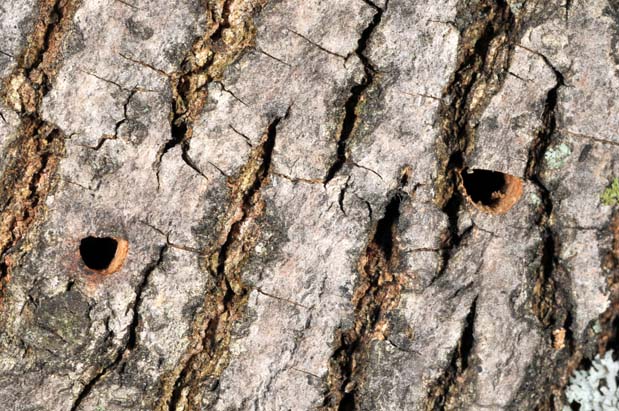
Emerald Ash Borer damage
(John Obermeyer, Purdue University) |
|
Common Name: Emerald Ash Borer - damage
See also: adult | larva Scientific Name: Buprestidae: Agrilus planipennis Status: devastating introduced pest of ash trees Damaging Stage: larval Injury: The larvae bore through the bark of ash trees and feed for several weeks beneath the bark of ash trees, leaving characteristic S-shaped tunnels. These tunnels eventually kill the tree. Emerald ash borers leave a characteristic D-shaped exit hole in the bark when they emerge as adults. Action Threshold: Prevention is the best approach. Being aware of when and where the beetle is active and implementing preventative controls is the only strategy for many. Once a tree becomes infested with emerald ash borers it is often too late to save. Management: Governmental programs of destroying infested trees in an effort to contain or eradicate the beetles are ongoing. Unfortunately, emerald ash borers often are artificially spread by people who unwittingly move borer-infested nursery stock or firewood from infested to uninfested areas. Education and regulations are excellent ways to slow the spread of this pest. Once trees are infested their prognosis is grim. Chemical controls are not always successful and are extremely labor-intensive and expensive. |
 |
||||||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||
|
Purdue Extension Entomology, 901 West State Street, West Lafayette, IN 47907 USA, (765) 494-4554 Department of Entomology | College of Agriculture | Extension © Purdue University | An equal access/equal opportunity university | Integrity Statement | Copyright Complaints | Maintained by ENTM IT Trouble with this page? Disability-related accessibility issue? Please contact us at entmwebmaster@purdue.edu so we can help. | ||||||||||||||||