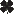|
|
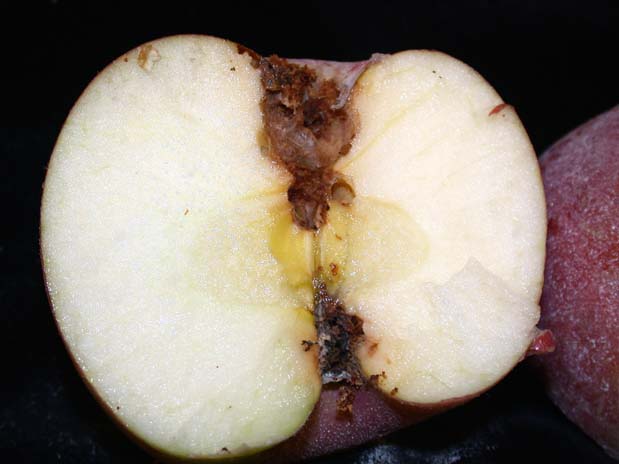
Codling Moth damage
(John Obermeyer, Purdue University) |
|
Common Name: Codling Moth - damage
See also: adult | larva Scientific Name: Tortricidae: Cydia pomonella Status: pest of fruits and nuts Damaging Stage: caterpillar Injury: Larvae typically tunnel to the core of the fruit. The tunnel entrances are surrounded with red-brown, crumbly, frass deposits. Infested fruit is considered “wormy” and unfit for human consumption. Action Threshold: Pheromone traps can be used to monitor codling moth activity. Trees should be treated when five or more adult moths are captured in baited traps that sample an area of five to ten acres. Management: Some biological controls can help lower a population initially but they cannot effectively suppress a severe codling moth infestation. Chemical controls are usually the best option in these situations. Proper timing of pesticide applications is critical for effective codling moth control. |
 |
||||||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||
|
Purdue Extension Entomology, 901 West State Street, West Lafayette, IN 47907 USA, (765) 494-4554 Department of Entomology | College of Agriculture | Extension © Purdue University | An equal access/equal opportunity university | Integrity Statement | Copyright Complaints | Maintained by ENTM IT Trouble with this page? Disability-related accessibility issue? Please contact us at entmwebmaster@purdue.edu so we can help. | ||||||||||||||||