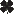| Diptera - true flies | ||||||||
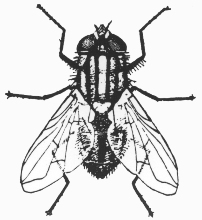 House fly Muscidae 1/4 in. 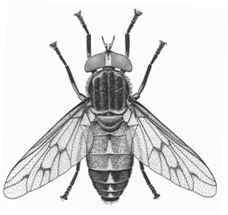 Horse fly Tabanidae 7/8 in. |
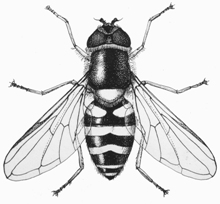
Syrphid fly Syrphidae 3/8 in. |
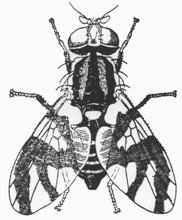
Fruit fly Tephritidae 1/4 in. |

Bee fly Bombyliidae 5/8 in. |
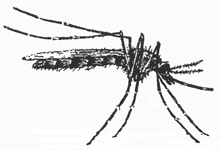
Mosquito Culicidae 3/8 in. |
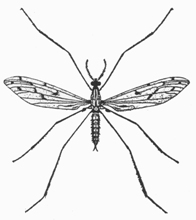
Crane fly Tipulidae 1/2 in. |
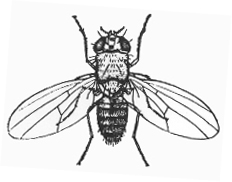
Vinegar fly Drosophilidae 1/16 in. |

Robber fly Asilidae 7/8 in. |
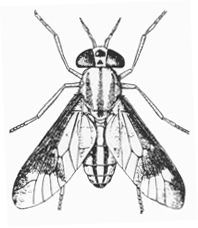
Deer fly Tabanidae 3/8 in. |