4-H and Youth  |
| Home |
| How to Know Insects |
| How to Collect Insects |
| How to Preserve Insects |
| How to Display Insects |
| How to Identify Insects to Order |
| Field Identification |
| Where to Get Supplies |
| Reference Books |
| Insect Collection Checklist |
| Order Labels |
| Specimen Labels |
| Insect Card Points |
|
|
|
|
Hymenoptera - bees, wasps, ants, sawflies, and hymenopterous parasites
|
 |
|
 Ant
Ant
Formicidae
1/4 in.
 Honey bee
Honey bee
Apidae
1/2 in.
Hymenopterans usually have four membranous wings, but some, such as worker ants, are wingless. If wings are present, they have few cross veins and the hind pair of wings is usually shorter than the front pair. Most Hymenoptera have chewing mouthparts, but, in bees and wasps, the lower "lip" may be prolonged into a "tongue." All Hymenoptera, except the sawflies and horntails, have the abdomen constricted or "pinched" where it joins the thorax. Metamorphosis is complete.
Many adult Hymenoptera can be found near flowers or other plant material where they come to feed. The larvae of ants, bees, and wasps are found in the nest or hive, but those of sawflies feed on plants and so are more exposed. Some species of wasps are parasitic on other insects and are valued as effective natural control agents. Many bees, including the honey bee, are highly beneficial as plant pollinators.
|

Bumble bee
Apidae
7/8 in.
|
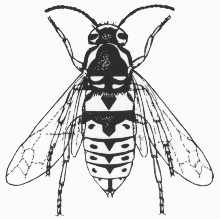
Yellow jacket
Vespidae
5/8 in.
|
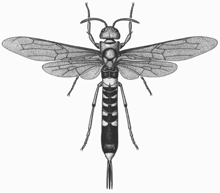
Horntail
Siricidae
1 1/4 in.
|

Velvet ant
Mutillidae
1/2 in.
|

Cicada killer wasp
Sphecidae
1 3/8 in.
|

Mud dauber wasp
Sphecidae
1 in.
|
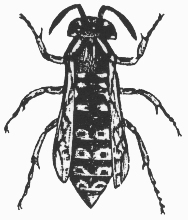
Hornet
Vespidae
3/4 in.
|
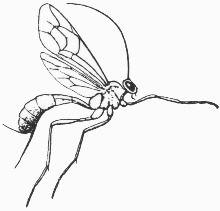
Ichneumon wasp
Ichneumonidae
3/8 in.
|
|
|
|